Hard Start
Checks
| Action
|
DEFINITION: The engine
cranks OK, but does not start for a long time. The engine does eventually
run, or may start, but immediately dies.
|
Preliminary
Checks
| Refer to
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
.
| • | Make sure the driver is using the correct starting procedure. |
|
Sensor Checks
|
| • | Inspect for a shifted or fixed engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor. Test the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor using a scan tool
to compare the engine coolant temperature with the ambient air temperature
on a cold engine. If the coolant temperature reading is 5°C (9°F)
more or less than the ambient air temperature on a cold engine, check
for a high resistance in the coolant sensor circuit or the sensor itself.
Refer to
Temperature Versus Resistance
. |
| • | Check the throttle position (TP) sensor. A sticking throttle shaft
or a binding throttle linkage will causes a high TP sensor voltage (open throttle
indication). Under these conditions the PCM may not control the idle.
Monitor the TP sensor voltage with the scan tool or a voltmeter.
The indicated voltage should be less than 1.25 volts with
throttle closed. |
|
Fuel System Checks
|
| • | Check the fuel pump check valve. A faulty in tank fuel pump check
valve will allow the fuel in the lines to drain back to the tank after
stopping the engine. This condition is especially troublesome on hot
soak restarts. In order to check for this condition perform the
following steps: |
| - | Disconnect the fuel line at the fuel filter. |
| - | Remove the fuel tank filler cap. |
| - | Connect a radiator test pump to the fuel line and apply 102 kPa
(15 psi) of pressure. The check valve is OK if the pressure holds for
60 seconds. |
|
Ignition System Checks
|
| • | Check for the proper secondary voltage output with a J 26792
spark tester, or equivalent. |
| • | Check the spark plugs for any of the following conditions: |
| - | Wet (fuel fouled) spark plugs |
| - | A terminal screw that is bent or loose (rotate and pull) |
| - | A ceramic insulator that has cracks, carbon tracking or deposits
(red or black dust) |
| - | A tip insulator that has cracks, carbon tracking, deposits (oil,
carbon, glazing, fuel additive), or is loose (rattles) |
| - | A center electrode that is loose (wiggles side to side) |
| - | An incorrect spark plug gap that is too large or too small |
| - | Platinum pads that are missing |
| - | Check for bare or shorted ignition wires at cylinders 1 and 3
or cracked ignition boots at cylinders 2 and 4 |
| - | Check for loose ignition coil connections |
|
Additional Checks
|
| • | Check for no crank signal to the PCM. In order to provide improved
cold engine starting, the PCM delivers a richer fuel injector pulse on a cold
engine when the crank signal is present. Observe the Starter Switch
parameter on the scan tool while cranking the engine. A faulty crank
signal circuit will NOT cause a no start, only a longer start time under
harsh conditions. |
| • | Check the PCM grounds and engine grounds for clean and tight connections
in the correct locations. Refer to
Power and Ground
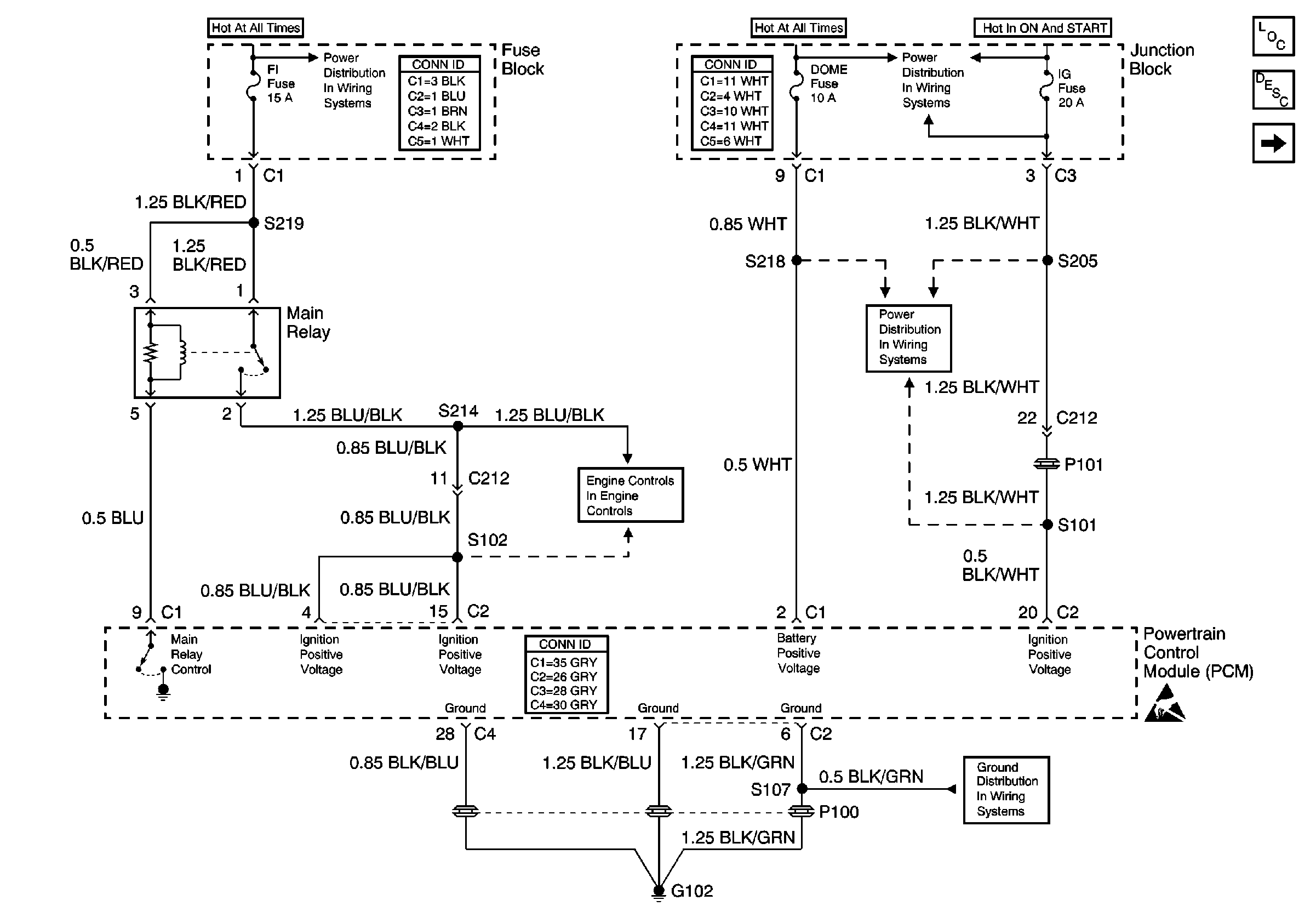
. |
| • | Check for service bulletin updates or information. |
|

