| Table 1: | IAC Valve Terminal (Pin) Location |
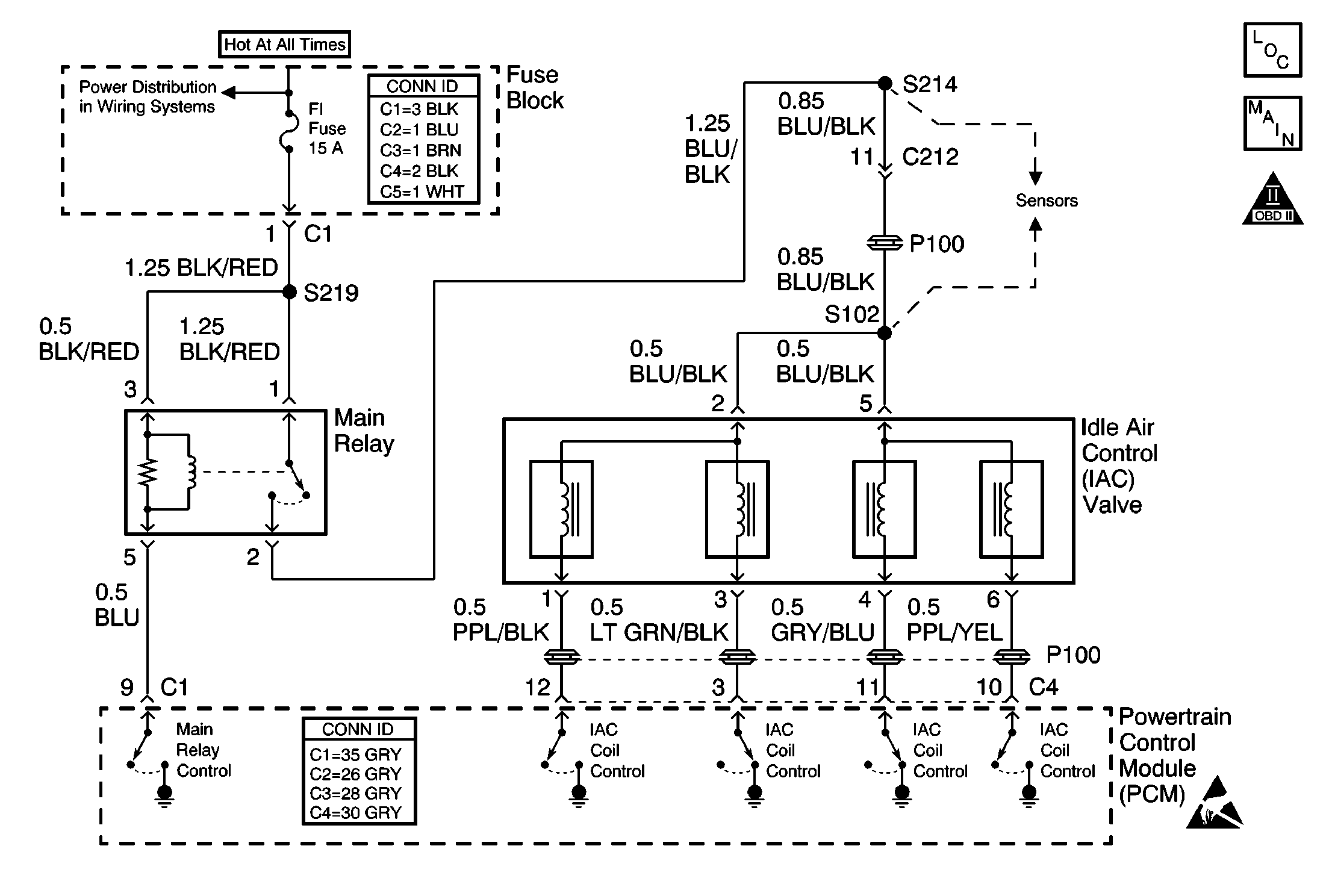
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the idle air control (IAC) valve in order to regulate the air flow through the idle air bypass passage. The amount of air flowing through the idle air bypass passage determines the idle speed. The PCM directs the IAC valve according to changes in engine load. A stalling or poor idle concern could be caused by an IAC valve that is not operating properly.
Diagnostic Aids
Any condition that can affect engine performance at idle, can affect the performance of the IAC system. A careful visual/physical inspection of the engine is necessary when the scan tool indicates that the Engine Speed or the IAC Duty Cycle readings are out of range.
A warm engine that is idling too slow, with a high IAC Duty Cycle (50 percent or more), may have an open in the ignition positive voltage circuit to terminal 5.
A warm engine that is idling too fast, with a low IAC Duty Cycle (15 percent or less), may have an open in the ignition positive voltage circuit to terminal 2.
An intermittent IAC system concern may be caused by poor electrical connections in the IAC valve circuits.
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing an intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating of terminals |
| • | Broken electrical connector locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Improper terminal to wire connections |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals |
Refer to the following procedures in Wiring Systems:
Use the following table in order to locate the correct terminals to test during diagnosis. The table layout corresponds to the pin location of the IAC valve electrical terminals.
Lock Tab | ||
3 | 2 | 1 |
6 | 5 | 4 |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step tests whether the PCM can operate the IAC valve with the scan tool. The IAC valve can be commanded to increase/decrease engine speed by using the scan tool's RPM control function. The RPM control function of the scan tool is disabled when any DTCs are set, and when the engine is below the normal operating temperature of 80°C (176°F).
-
This step checks the operation of the electrical load idle-up circuits. If there is no increase in the IAC Duty Cycle percentage when the accessory is turned ON, the idle-up circuit may be inoperative or always ON.
-
This step checks the operation of the A/C idle-up circuits. If there is no increase in the IAC Duty Cycle percentage when the A/C compressor is engaged, the idle-up circuit may be inoperative or always ON.
-
This step checks the electrical circuits between the IAC valve and the PCM.
-
This step checks whether the PCM is attempting to control the IAC valve. Each IAC coil control circuit should indicate high voltage (12 volts or more) and then low voltage (0.0-1.0 volts) as the PCM commands changes in the engine speed. Remember to clear any DTCs and run the engine to normal operating temperature before attempting RPM control with the scan tool.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||||
2 | Is there a CURRENT or PENDING DTC P0505 set? | -- | ||||||||||
3 |
Are the Engine Speed and IAC Duty Cycle within the specified values? | 700-800 RPM in Neutral 10% to 30% IAC Duty | ||||||||||
Did the engine speed increase and decrease when commanded by the scan tool? | -- | |||||||||||
Did the Engine Speed stay within the specified values while the IAC Duty Cycle increased 2 to 3 percent? | 700-800 RPM in Neutral | |||||||||||
Turn ON the HVAC blower motor and the air conditioning, if equipped. Is the Engine Speed within the specified values and did the IAC Duty Cycle increase 4 to 12 percent when the A/C compressor was operating? | 800-900 RPM in Neutral | |||||||||||
7 |
Are the Engine Speed and IAC Duty Cycle within the specified values? | 700-800 RPM in Neutral 10% to 30% IAC Duty | System OK | |||||||||
8 |
Was the resistance measured within the specified values? | 35-43 ohms at 20°C (68°F) | ||||||||||
9 |
Did the test lamp illuminate for both circuits? | -- | ||||||||||
Was the voltage of each IAC coil control circuit more than the specified value? | 12 volts | |||||||||||
Was the voltage of each IAC coil control circuit switching from high to low while increasing and decreasing the engine speed? | -- | |||||||||||
12 | Repair the high resistance or open in the ignition positive voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
13 | Repair the short to ground, open circuit, or high resistance in any IAC coil control circuit that did not measure at least 12 volts in step 10. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
14 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||
15 | Replace the IAC valve. Refer to Idle Air Control Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
16 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
17 | Operate the vehicle within the conditions in which the customer concern was first noticed. Is the concern still present? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
