Checks
| Action
|
DEFINITION: The engine power output varies under a steady
throttle or cruise. The vehicle seems to speed up and slow down with no
change in the accelerator pedal position.
|
Preliminary
Checks
|
| • | Educate the driver about normal A/C compressor operation. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to verify that the reading of vehicle
speed sensor (VSS) matches the reading of the vehicle speedometer. Vehicles
with electronic transmissions are excluded because some variation between
VSS readings and speedometer readings are considered normal. |
|
Sensor Check
|
| • | Inspect the performance of the heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) 1.
Refer to: |
| • | Inspect for a shifted or fixed engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor. Test the ECT sensor using the scan tool. Compare the engine coolant
temperature with the ambient air temperature on a cold engine. If
the engine coolant temperature is more than 5°C (9°F) more or less
than the ambient air temperature, check for a high resistance in the coolant
sensor circuit or the sensor itself. Refer to
Temperature Versus Resistance
. |
| • | Check the CMP sensor engine reference signal with a scan tool.
Observe the Engine Speed parameter while operating the engine at the speed
of the concern. The scan tool should indicate steady and linear RPM
readings while running. If the erratic values, such as sudden spikes
or drops in engine speed are displayed, the engine reference signal
is not stable enough for the engine to run properly. Inspect the camshaft
position (CMP) sensor signal rotor and housing for worn bushings or drive
coupling. Inspect for electromagnetic interference (EMI) of the reference
signal. |
|
Fuel System Checks
|
| • | Determine whether a rich or lean fueling condition can cause the
concern. Drive the vehicle at the speed of the concern. Monitor the Fuel Trim
parameters on a scan tool in order to identify the fuel system status. |
|
Ignition System Checks
|
| • | Check for adequate secondary ignition voltage with a J 26792
spark tester or an equivalent. |
| • | Check the spark plugs for any of the following conditions: |
| - | A terminal screw that is bent or loose |
| - | A ceramic insulator that has cracks, carbon tracking or deposits |
| - | A tip insulator that has cracks, carbon tracking, deposits, or
is loose |
| - | A center electrode that is loose |
| - | An incorrect spark plug gap that is too large or too small |
|
Additional Checks
|
| • | Verify the PCM grounds are clean, tight, and in the proper locations.
Refer to
Power and Ground
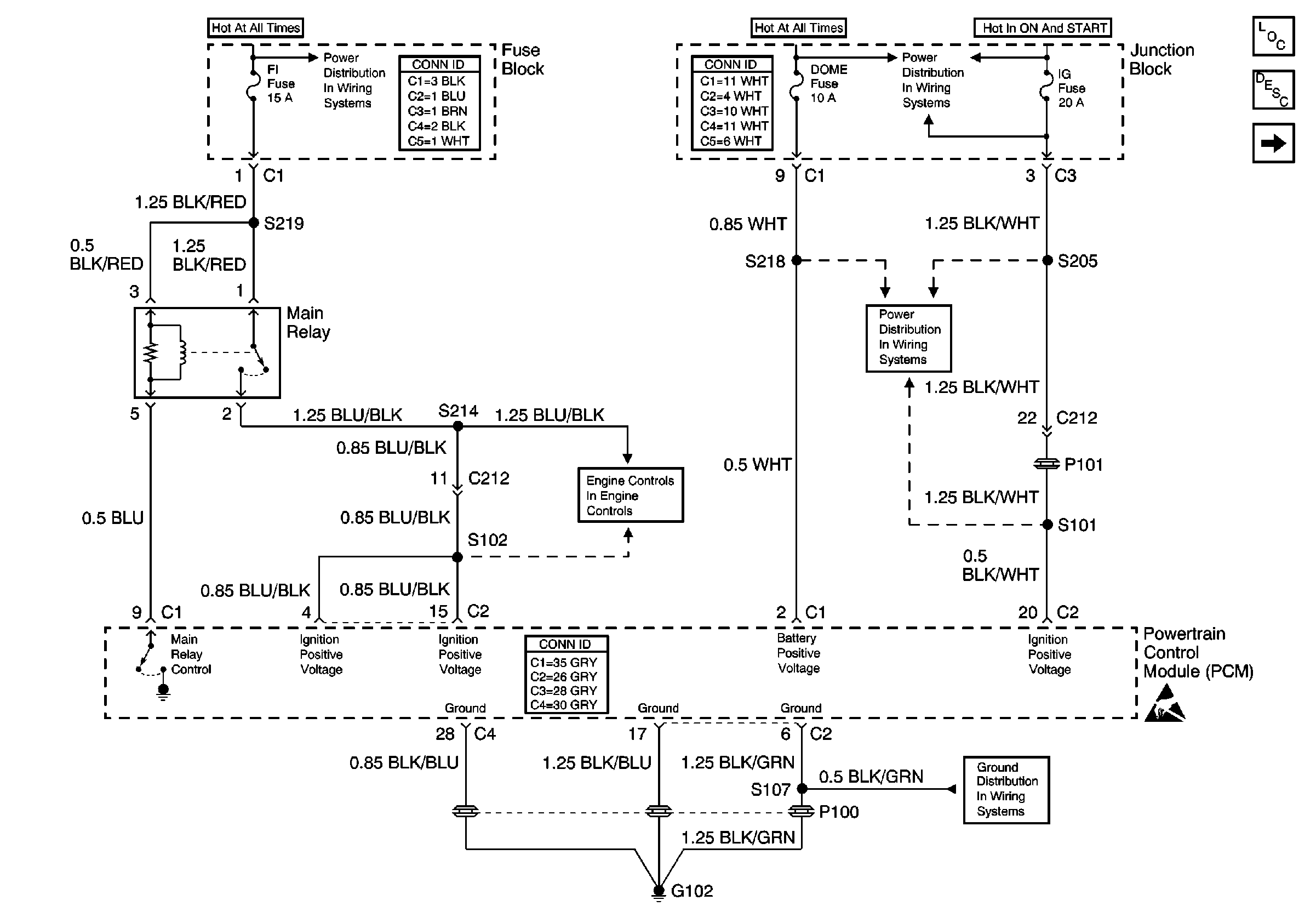
. |
| • | Check the generator output voltage. |
| • | Check the vacuum lines and hoses for kinks, leaks, and correct
routing. |
| • | Check the Service Bulletins for any updates. |
|

