Circuit Description
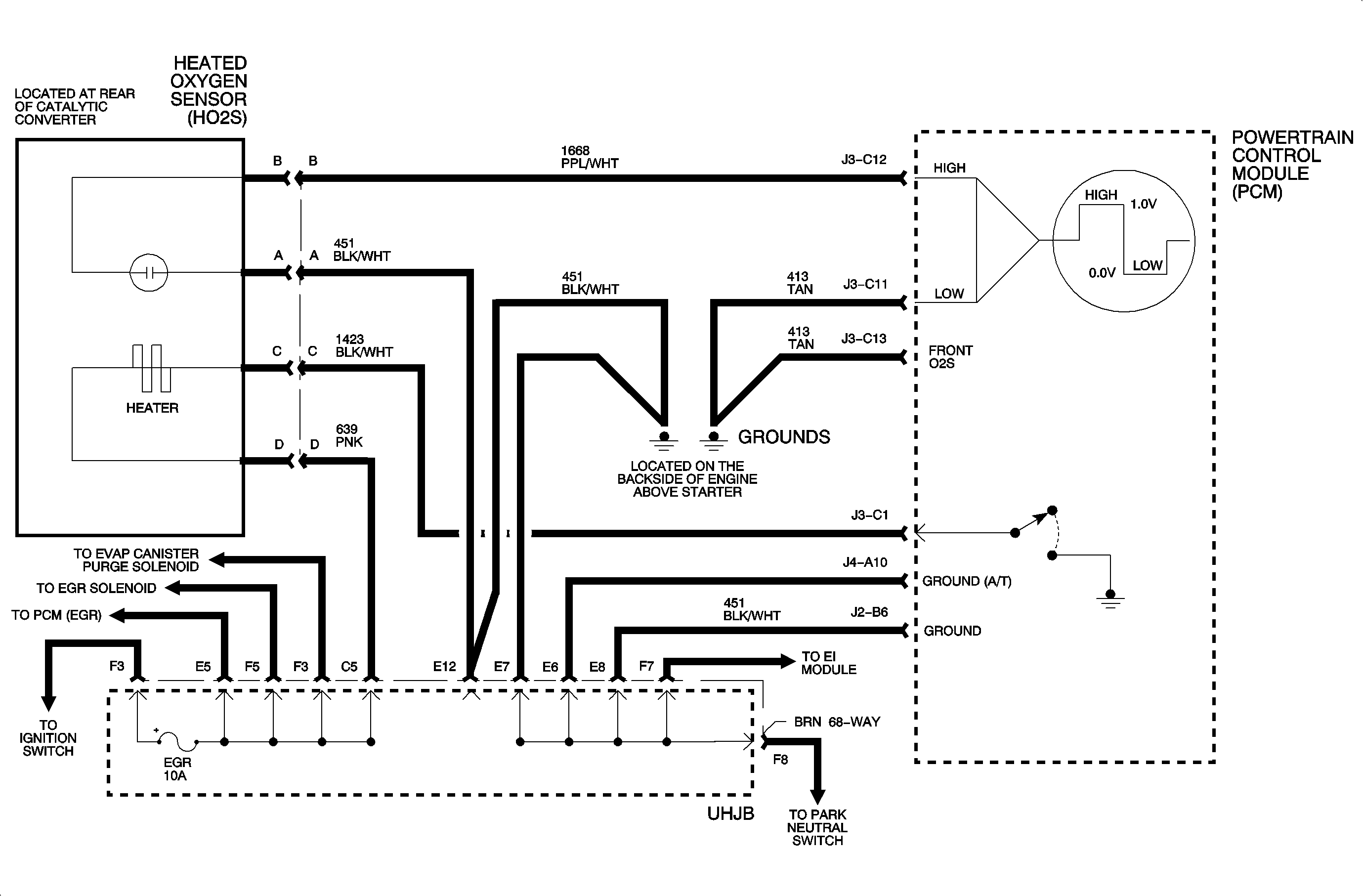
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) consists of a zirconia electrolyte between 2 platinum plates. When the sensor reaches approximately 318°C (600°F), it becomes an electrical source that responds to the oxygen content in the exhaust. The PCM produces a bias voltage of approximately 450 millivolts on the oxygen sensor circuit. When the sensor is cold, its internal resistance is extremely high, therefore the PCM recognizes the bias as an open circuit. As the sensor warms up, the internal resistance decreases. When the sensor reaches approximately 318°C (600°F), it starts producing a voltage based on the oxygen content in the exhaust stream.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Important: The HO2S signal is continuously checked once the above conditions have been met.
DTC P0140 will set if the HO2S voltage is between 391-491 mV for 90 seconds when:
| • | The engine is at normal operating temperature, and the ECT reads over 60°C (140°F). |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 1 minute. |
| • | No other engine sensor or misfire DTCs have been set. |
| • | The commanded A/F ratio is approximately 14.7:1. |
Diagnostic Aids
If a DTC P0141, heater malfunction, is also set, repair that code first. An inoperative heater may cause the sensor to cool down, which may cause the inactive DTC to set.
The PCM will not perform a catalyst monitor test if a DTC P0140 is set.
Normal scan tool readings in closed loop will show the oxygen sensor voltage varying between 10-999 mV.
Important: Do not apply grease or any material in the HO2S connector or alter the wiring in any way. The wires carry reference air to the sensor used to determine the difference in oxygen from the exhaust gas to the PCM.
DTC P0140 can set or cause false oxygen sensor readings if the oxygen sensor ground becomes loose. Refer to PCM and Engine Grounds.

