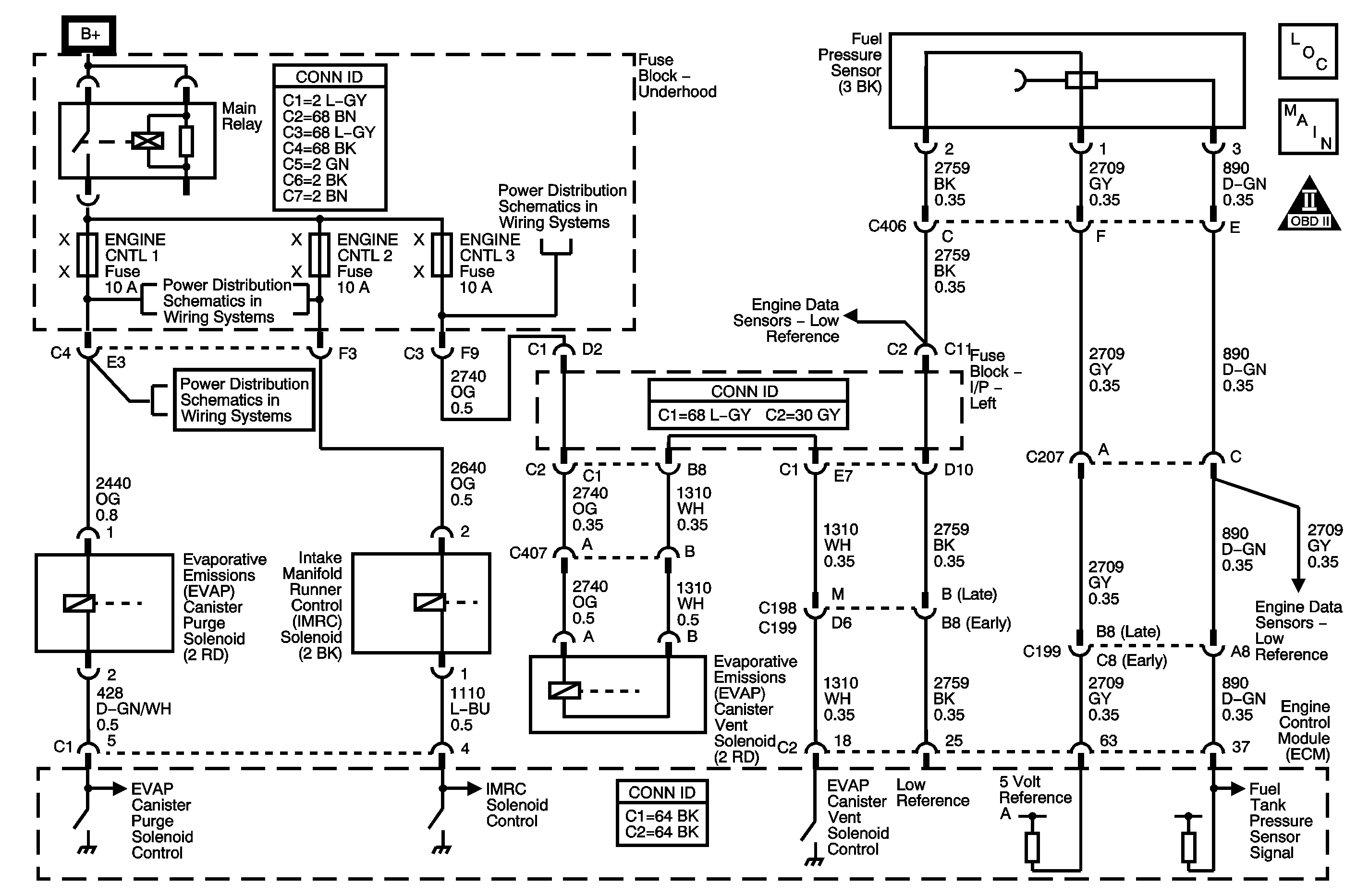
System Description
The evaporative emission (EVAP) system is used to store fuel vapors as to reduce the amount of unburned fuel from escaping into the atmosphere. The EVAP system consists of the EVAP canister, fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor, EVAP lines and hoses, EVAP purge solenoid (normally closed), EVAP service port, EVAP vent solenoid (normally open) and fuel tank. The engine control module (ECM) monitors the EVAP system for circuit faults in the EVAP purge solenoid, EVAP vent solenoid and FTP sensor circuits. The ECM also monitors the EVAP for leaks between EVAP vent and purge solenoid. When certain conditions have been met, the ECM will perform an EVAP diagnostic test at idle with no vehicle speed. DTC P0455 will set if a vacuum cannot be pulled on the EVAP system during the EVAP diagnostic system test indicating a large EVAP system leak or insufficient vacuum to EVAP purge solenoid.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0036, P0037, P0038, P0050, P0051, P0052, P0056, P0057, P0058, P0116, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0128, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0135, P0136, P0137, P0138, P0139, P0140, P0141, P0150, P0151, P0152, P0153, P0154, P0155, P0156, P0157, P0158, P0159, P0160, P0161, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0442, P0443, P0444, P0445, P0446, P0447, P0448, P0449, P0451, P0452, P0453, P0506, P0507, P1271, P1277, P1278, P1282, P1283, P1511, P1516, P1519, P1523, P1526, P1530, P1551, P2100, P2101, P2107, P2119, P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128, P2138, P2176 are not set. |
| • | The condition exists for 15 seconds or no change is detected for 4 seconds. |
| • | The EVAP purge solenoid is commanded to a 20 percent duty cycle. |
| • | The EVAP vent solenoid is commanded ON. |
| • | The engine is at idle. |
| • | The vehicle speed is 0 km/h (0 mph). |
| • | The engine load is less than 35 percent. |
| • | The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) is less than 40 kPa. |
| • | The battery voltage is greater than 11 volts. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) at engine startup is between 8-75°C (46-167°F). |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) is between 8-75°C (46-167°F). |
| • | The long term FT cells learned (if not learned, engine must run longer than 16 minutes and 45 seconds). |
DTC P0455 diagnostic runs once during Phase D of the EVAP diagnostic test once per ignition cycle. If DTC P0455 fails, the ECM will re-run the EVAP diagnostic test from the beginning and must fail P0455 again to set.
If an EVAP diagnostic test is aborted due to changing enabled criteria, the ECM will run the entire EVAP test up to three times per ignition cycle.
Conditions For Setting the DTC
DTC P0455 will set if the FTP cannot be pulled lower than 2.02 volts, -4.50 mm Hg (-2.41 in H20), during the EVAP diagnostic system test indicating a large EVAP leak.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A current DTC Last Test Failed clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If DTC P0440, P0442, P0446, P0455 is set, EVAP special functions on the scan tool will not be allowed. Clear DTCs before performing these tests. |
| • | The ECM uses the FTP sensor to detect the pressure of fuel vapor in the fuel tank during all parts of the EVAP diagnostic system test. Ensure the FTP sensor is not skewed by verifying FTP Sensor on the scan tool is between 2.35-2.85 volts with the ignition ON and the engine OFF. |
| • | Possible causes of a large EVAP leak: |
| • | The fuel cap is missing, incorrectly installed or leaking. |
| • | The EVAP vent solenoid valve stuck open. |
| • | The EVAP purge solenoid stuck closed/blocked or lack of manifold vacuum to solenoid. |
| • | The EVAP line/hose connections are disconnected/leaking. |
| • | The fuel sender O-ring is leaking. |
| • | The FTP sensor seal is leaking. |
| • | To help locate intermittent leaks, use the J 41413-200 (J 41413-100) Evaporative Emissions System Tester (EEST) to introduce smoke into the EVAP system. Move all EVAP components while observing smoke with the High Intensity White Light. |
| • | To improve the visibility of the smoke exiting the EVAP system, observe the suspected leak area from different angles with a High Intensity White Light. |
| • | Review the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition. |
| • | For intermittent conditions refer to Intermittent Conditions . |
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Evaporative Emissions Hose Routing Diagram | ||||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||
2 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the Service Bay Test passed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||
3 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||||
4 |
Important: Ensure that the vehicle underbody temperature is similar to the ambient temperature and allow the surrounding air to stabilize before starting the diagnostic procedure. System flow will be less with higher temperatures.
Did you locate and repair a leak source? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||||
5 |
Did you locate and repair a leak source? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||||
6 |
Is the scan tool Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter within the specified value of the J 41413-200 (J 41413-100) pressure/vacuum gage? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||||
7 |
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter more than the second specified value? | 10 in H2O 5 in H2O | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||||
8 |
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 9 | ||||||||||
9 | Disconnect the EVAP purge vacuum source from the EVAP purge solenoid. Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||
10 | Disconnect the EVAP purge pipe from the EVAP purge solenoid. Is the Fuel Tank Pressure sensor parameter Less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||||
11 | Disconnect the EVAP purge pipe at the EVAP canister. Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 12 | ||||||||||
12 | Disconnect the EVAP vapor pipe at the EVAP canister. Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||
13 | Repair the pinched or obstructed EVAP purge solenoid vacuum source. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
14 | Repair the pinched or obstructed EVAP vapor pipe. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
15 | Repair the restriction in the EVAP purge pipe. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
16 | Replace the FTP sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
17 | Replace the EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
18 | Replace the EVAP canister. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
19 | Perform the Service Bay Test. Refer to Service Bay Test . Does the scan tool indicate that the Service Bay Test passed? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||
20 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |||||||||||
