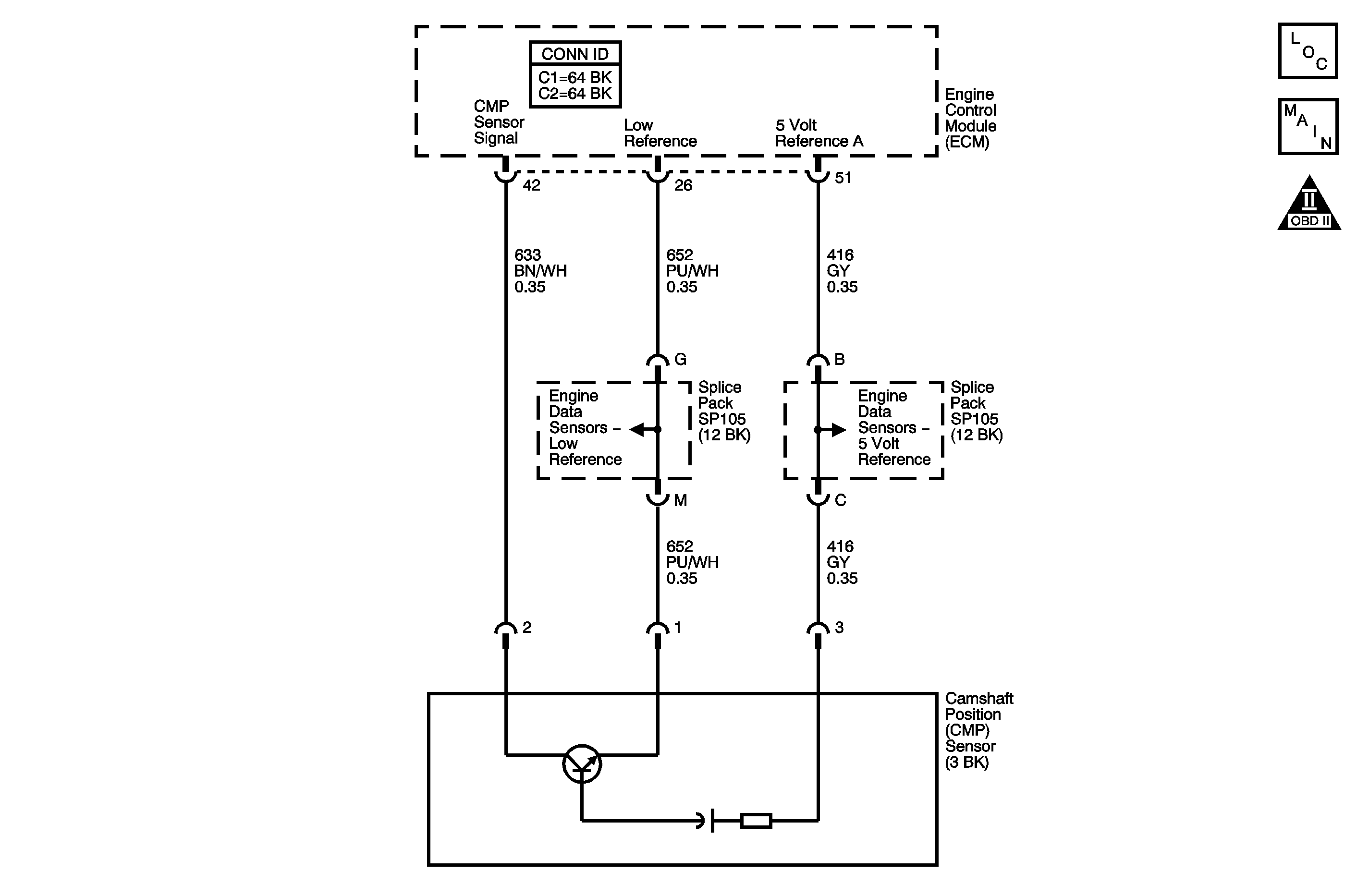
Circuit Description
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is a hall effect switching device that works in conjunction with a single tooth reluctor wheel used to determine the position of the bank 2 exhaust camshaft. The engine control module (ECM) expects the CMP sensor signal to be low, 0 volts, as the single tooth in the reluctor wheel passes the sensor, and high, 5 volts, during the remainder of the reluctor wheel rotation. The ECM supplies a 5-volt pull up voltage on the CMP sensor signal circuit. The ECM expects to see one transition from high to low every two crankshaft revolutions. This signal, when combined with the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor signal, enables the ECM to properly synchronize ignition timing, fuel delivery and knock control. As long as the CKP signal is available, the engine can start and run. The ECM will default to a non-sequential fuel injector operation even if there is no CMP sensor signal. If the ECM detects extra or missing CMP sensor signal transitions within a certain number of crankshaft revolutions, DTC P0341 sets.
The CMP sensor has the following circuits:
| • | 5-volt reference circuit |
| • | Low Reference circuit |
| • | CMP sensor signal circuit |
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The CMP signal is inconsistent for eight or more crankshaft revolutions.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The following conditions may cause this DTC to set: |
| - | Camshaft reluctor wheel damage |
| - | Incorrect sensor installation |
| - | The sensor coming in contact with the reluctor wheel |
| - | Excessive air gap between the reluctor wheel and the sensor magnet |
| - | A cracked or damaged sensor |
| - | Foreign material passing between the sensor and the reluctor wheel |
| • | This DTC will set with an intermittent failure on the ignition 1 voltage circuit, the CMP sensor signal circuit, or the low reference circuit. A hard failure of any one of these circuits should set DTC P0342 or P0343. |
| • | The CMP sensor low reference circuit is shared with the following sensors: |
| - | The mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
| - | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
| - | The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| - | The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) sensor |
| - | The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor |
| - | The throttle position (TP) sensor 1 |
| - | The TP sensor 2 |
| • | The CMP sensor 5-volt reference circuit is shared with the following sensors: |
| - | The EGR sensor |
| - | The MAF sensor |
| - | The MAP sensor |
| - | The air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensor |
| - | The fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor |
| - | The accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor 1 |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Control Module Connector End Views or Engine Controls Connector End Views | |||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | Go to Step 2 | |||||||
|
Important:: If DTC P0342 or P0343 is set, diagnose those DTCs first.
Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 3 | |||||||
3 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the CMP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||
4 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the engine control module (ECM). Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||
6 | Inspect the reluctor wheel for signs of damage or looseness. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. If you find damage or looseness to the reluctor wheel, refer to Camshaft Replacement - Left Side in Engine Mechanical. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||
7 | Replace the CMP sensor. Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||
8 | Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 9 | -- | ||||||
9 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||
10 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTC's that have not been diagnosed? | System OK | |||||||
