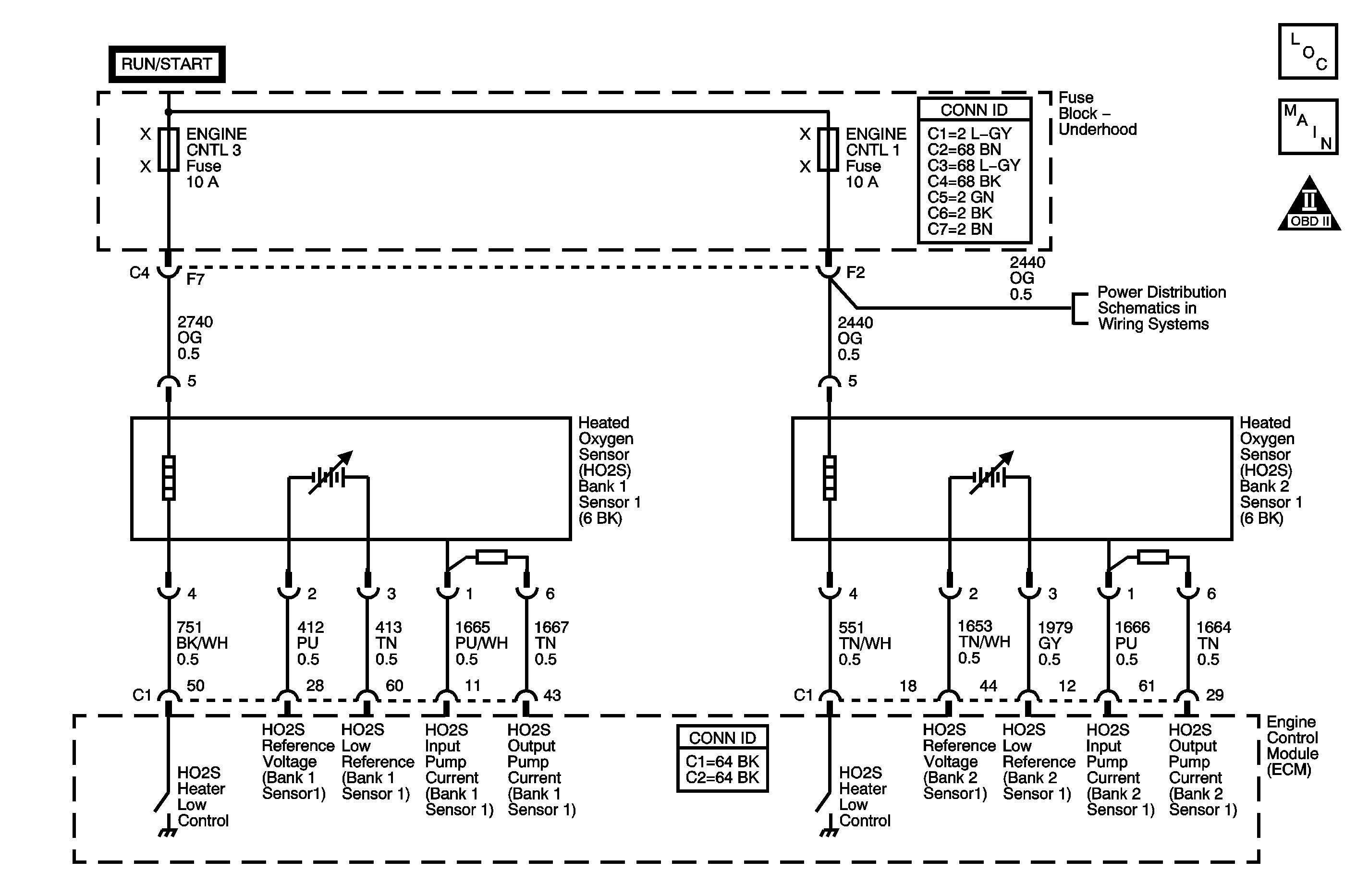
Circuit Description
The wide band heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream more quickly and accurately than the switching style HO2S. The wide band sensor consists of an oxygen sensing cell, an oxygen pumping cell, and a heater. The exhaust gas sample passes through a diffusion gap between the sensing cell and the pumping cell. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a signal voltage to the HO2S and uses this voltage as a reference to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system. An electronic circuit within the ECM controls the pump current through the oxygen pumping cell in order to maintain a constant signal voltage. The ECM monitors the voltage variation on the signal circuit and attempts to keep the voltage constant by increasing or decreasing the amount of current flow, or reversing the direction of the current flow to the pumping cell. By measuring the direction and amount of current required to maintain the signal voltage, the ECM can determine the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust. The signal voltage is displayed as a lambda value. A lambda value of 1 is equal to a stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1. Under normal operating conditions, the lambda value will remain around 1. When the system is lean, the oxygen level will be high and the lambda value will be high or more than 1. When the system is rich, the oxygen level is low and the lambda value will be low or less than 1. The ECM uses this information to maintain the proper air/fuel ratio. If the ECM detects a fault, DTC P0130 will set for bank 1 sensor 1, or DTC P0150 will set for bank 2 sensor 1.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0050, P0051, P0052, P0135, P0138, P0139, P0141, P0155, P0158, P0159, P0161 are not set. |
| • | The engine is running. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The ECM detects that one of the following relationships is true between the affected HO2S and the HO2S sensor on the same cylinder bank: |
| • | The affected HO2S signal voltage is more than 4.81 volts for more than 2 seconds. |
| OR |
| • | The affected HO2S lambda value is between 0.995-1.005, while the HO2S sensor 2 voltage is more than 0.850 volts or less than 0.103 volts. |
| OR |
| • | The affected HO2S lambda value is more than 1.2, and the HO2S sensor 2 is more than 0.850 volts for 2-16 seconds. |
| OR |
| • | The affected HO2S lambda value is less than 0.8, and the HO2S sensor 2 is less than 0.103 volts for 2-16 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls Connector End Views | ||||||||||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||||||||
2 |
Important: During idle or steady throttle conditions the lambda value will be very close to 1.000.
Is the HO2S lambda value varying within the specified range? | 0.900-1.100 | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||||||||||
3 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||||||||
4 |
Refer to Exhaust Leakage . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||||||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||||||||||
6 |
Is the HO2S lambda value less than the specified value? | 1.100 | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||||||||||
7 | Measure the voltage from the HO2S output pump current circuit, on the engine harness side, to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 4.8-5.1 V | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 9 | ||||||||||||||||
8 | Measure the voltage from the HO2S reference voltage circuit, on the engine harness side, to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 600 mV | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||||||||||
9 | Is the voltage less than the specified value? | 375 mV | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 17 | ||||||||||||||||
10 | Measure the voltage from the HO2S reference voltage circuit, on the engine harness side, to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 6 V | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||||||||
11 | Measure the voltage from the HO2S output pump current circuit, on the engine harness side, to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 330-360 mV | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||||||||
12 | Measure the voltage from the HO2S reference voltage circuit, on the engine harness side, to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 2.8-3.1 V | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 21 | ||||||||||||||||
13 |
Is the lambda value less than the specified value? | 3.500 | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 22 | ||||||||||||||||
14 | Is the voltage less than the specified value? | 330 mV | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 24 | ||||||||||||||||
15 |
Important: The normal voltage on the low reference circuit is 2.4-2.6 volts. Test the HO2S low reference circuit for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
16 | Test the following circuits for a short to ground:
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
17 |
Important: The normal voltage on the input pump current circuit and the output pump current circuit is 330-360 millivolts. Test the following circuits for a short to voltage:
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
18 | Test the HO2S low reference circuit for a high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
19 |
Important: The normal voltage on the reference voltage circuit is 2.8-3.1 volts. Test the HO2S reference voltage circuit for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
20 | Test the HO2S input pump current circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
21 | Test the HO2S reference voltage circuit for an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
22 | Test the following circuits for a short to the HO2S heater low control circuit:
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 26 | ||||||||||||||||
23 | Test the HO2S output pump current circuit for the following conditions:
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
24 | Test the following HO2S circuits for a short to any other HO2S circuit:
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||||||||||||
25 | Test for shorted terminals and poor connections at the engine control module (ECM). Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 28 | ||||||||||||||||
26 | The HO2S may be detecting a lean or rich exhaust condition. Inspect for one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 27 | ||||||||||||||||
27 | Replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 1 Sensor 1 or Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 2 Sensor 1 . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 29 | -- | ||||||||||||||||
28 | Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 29 | -- | ||||||||||||||||
29 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 30 | ||||||||||||||||
30 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |||||||||||||||||
