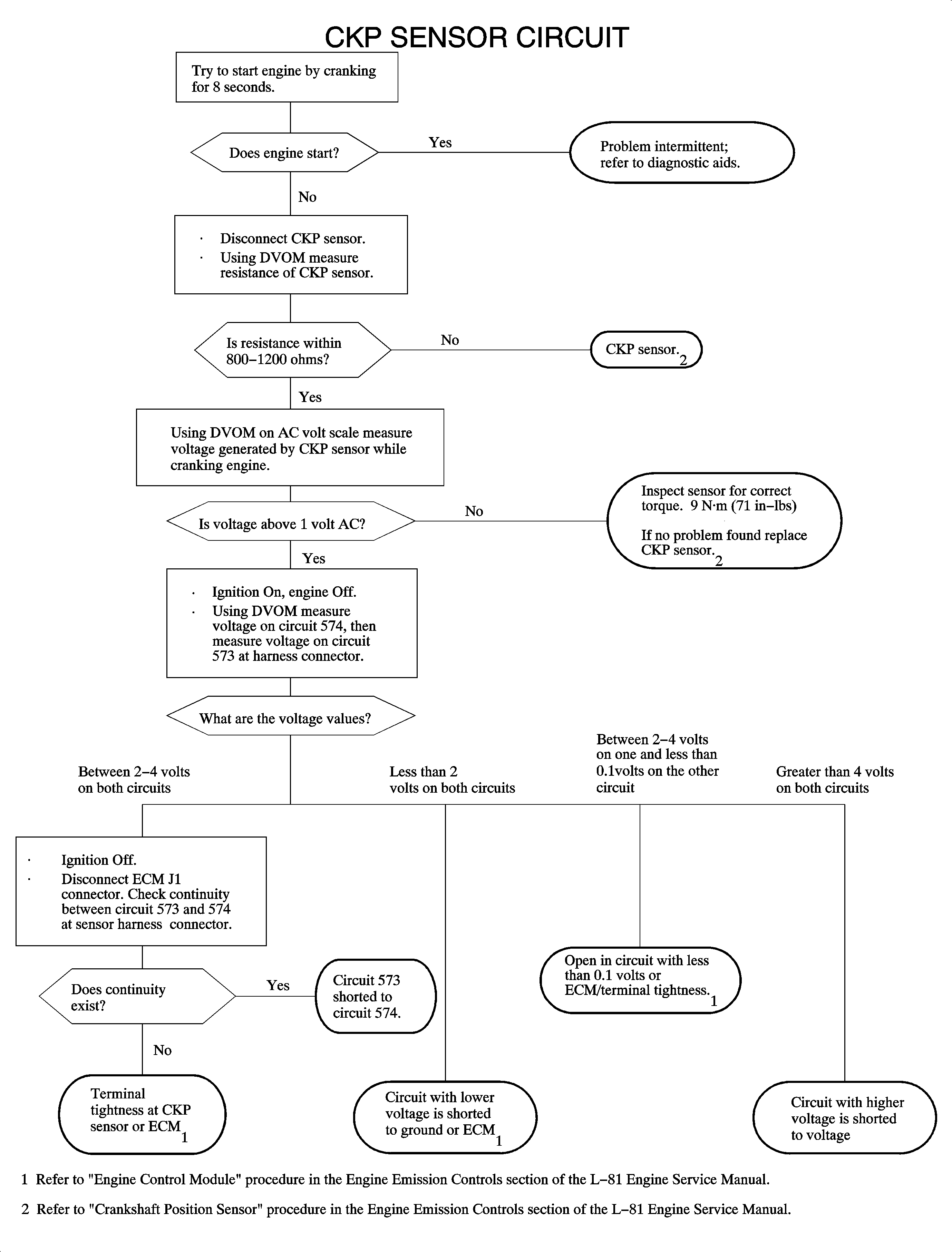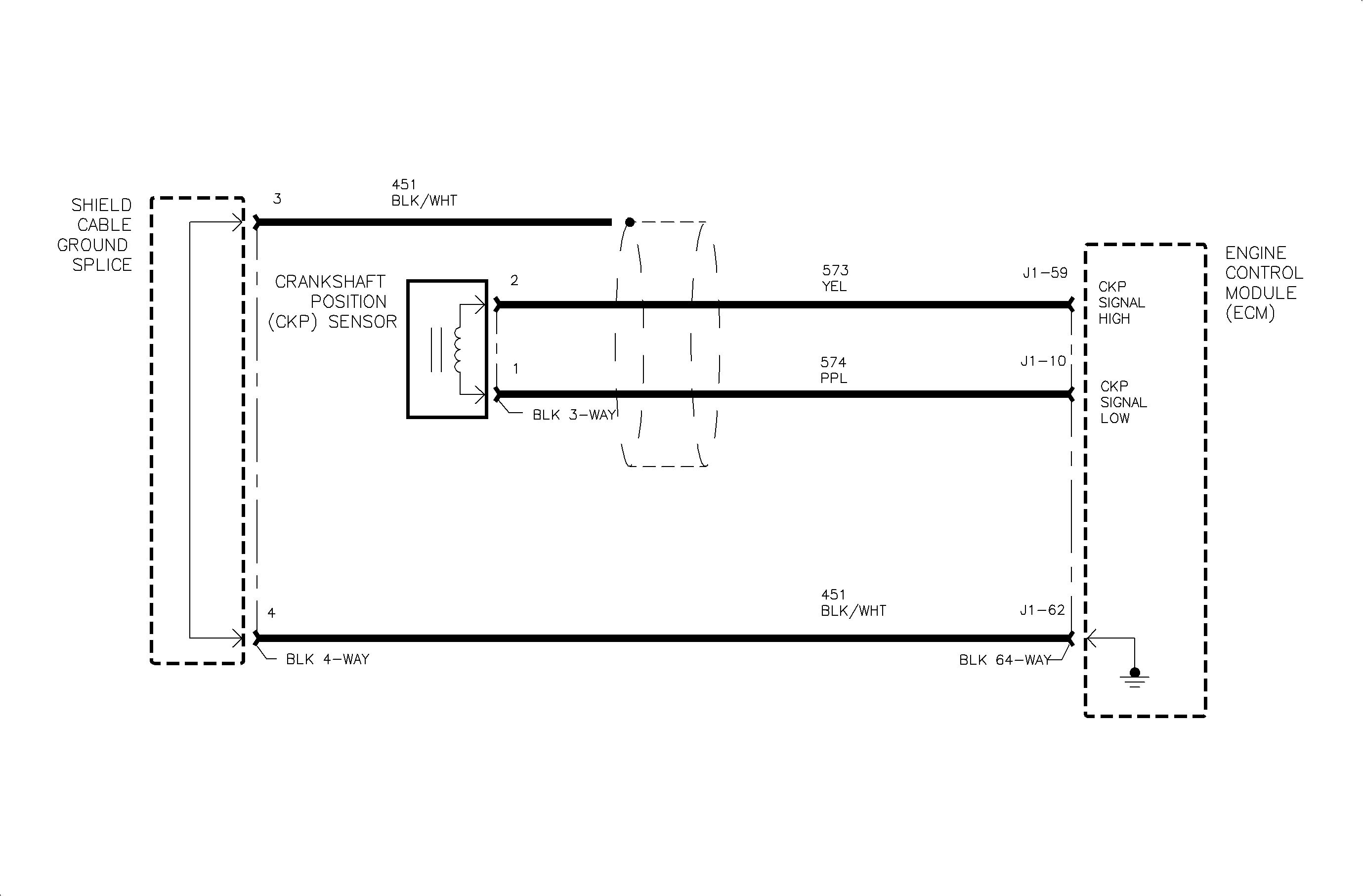
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor works in conjunction with a 58 tooth reluctor wheel on the crankshaft. As each reluctor wheel tooth rotates past the sensor, the sensor's internal circuitry causes a voltage to be applied to the signal circuit, creating a square wave used by the ECM. The reluctor wheel teeth are 6 degrees apart, which leaves a 12 degree span that is uncut. This creates a signature pattern that enables the ECM to determine the crankshaft position. The ECM can determine which two cylinders are approaching top center from the CKP alone. The camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal is used in order to determine which of the two cylinders is on a firing stroke. The ECM can then properly synchronize the ignition system, the fuel injectors and the knock control. This sensor is also used to detect misfire (refer to DTC P0300).
DTC Parameters
DTC P0335 will set if no engine speed (crank signal) is detected, but more than 8 phase level changes are detected from the CMP. A total of 16 crank rotations have to be missed for this code to set. Crank engine for longer than 5 seconds.
P0335 is a (type B) DTC
Diagnostic Aids
To locate an intermittent problem use scan tool to monitor the CMP resync counter with engine running (or while cranking).
While wires while monitoring CMP resync counter may locate area where a circuit fault may exist.
Important: Make sure the crankshaft position sensor circuit wires are clear of other voltage interfering wires. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) waves may offset a crankshaft signal to the ECM, setting a DTC.