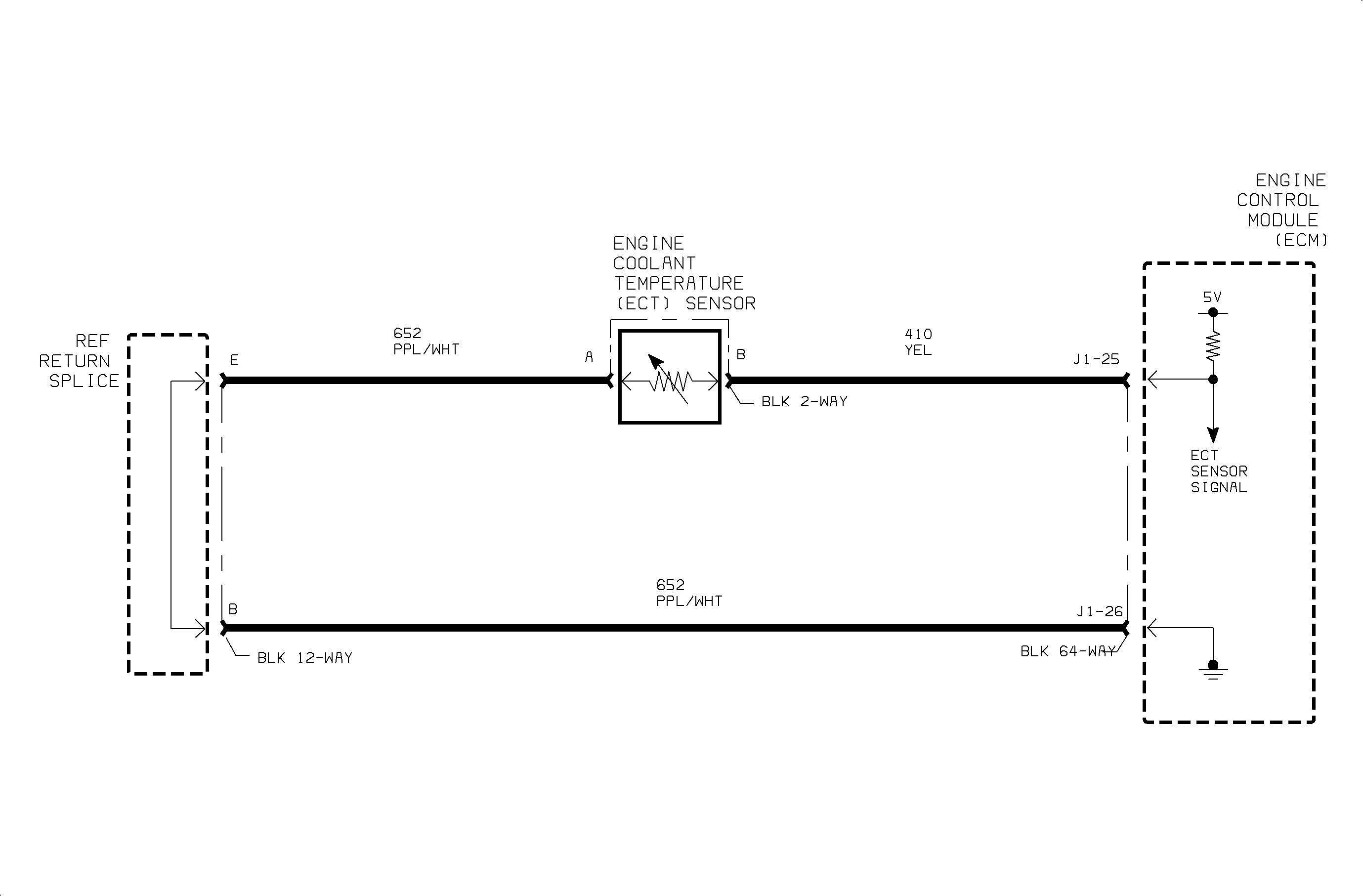
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a thermistor that is located in the lower coolant passage of the engine cylinder head. The ECM continuously monitors the voltage drop across the resistor as it varies with the resistance of the sensor. This sensor is used for fuel/ignition control, hot/low coolant light, coolant gage, and fan. A low voltage indicates a high temperature and vise-versa. The ECM sets this DTC when the signal being received deviates more than 12°C or 22°F from the ECM modeled temperature. The ECM continuously calculates this modeled temperature using ECT starting temperature, MAP, MAF, and engine run time.
DTC Parameters
This DTC will set when:
| • | Modeled and actual ECT difference greater than 12°C or 22°F |
| • | Engine running |
P0116 is a (type B) DTC.
Caution: To avoid the danger of being burned, do not remove the cap while the engine, radiator, and surge tank are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out under pressure.
Important: The ECT signal is continuously checked when ignition is On.
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0116 indicates that the ECT readings are valid but deviate more than 12°C or 22°F from the calculated value the ECM expects to see.
Possible causes:
| • | Shifted (skewed) sensor |
| • | Loose or intermittent connections in ECT circuit |
| • | Corrosion or resistance in ECT connector/wiring |
| • | Thermostat malfunction |
| • | Cooling fan malfunction |
| • | Extreme ambient temperature |
ECT may be compared to IAT with scan tool if engine has cooled overnight. They should be within 6°C or 10°F of each other with the ignition On and engine Off.
