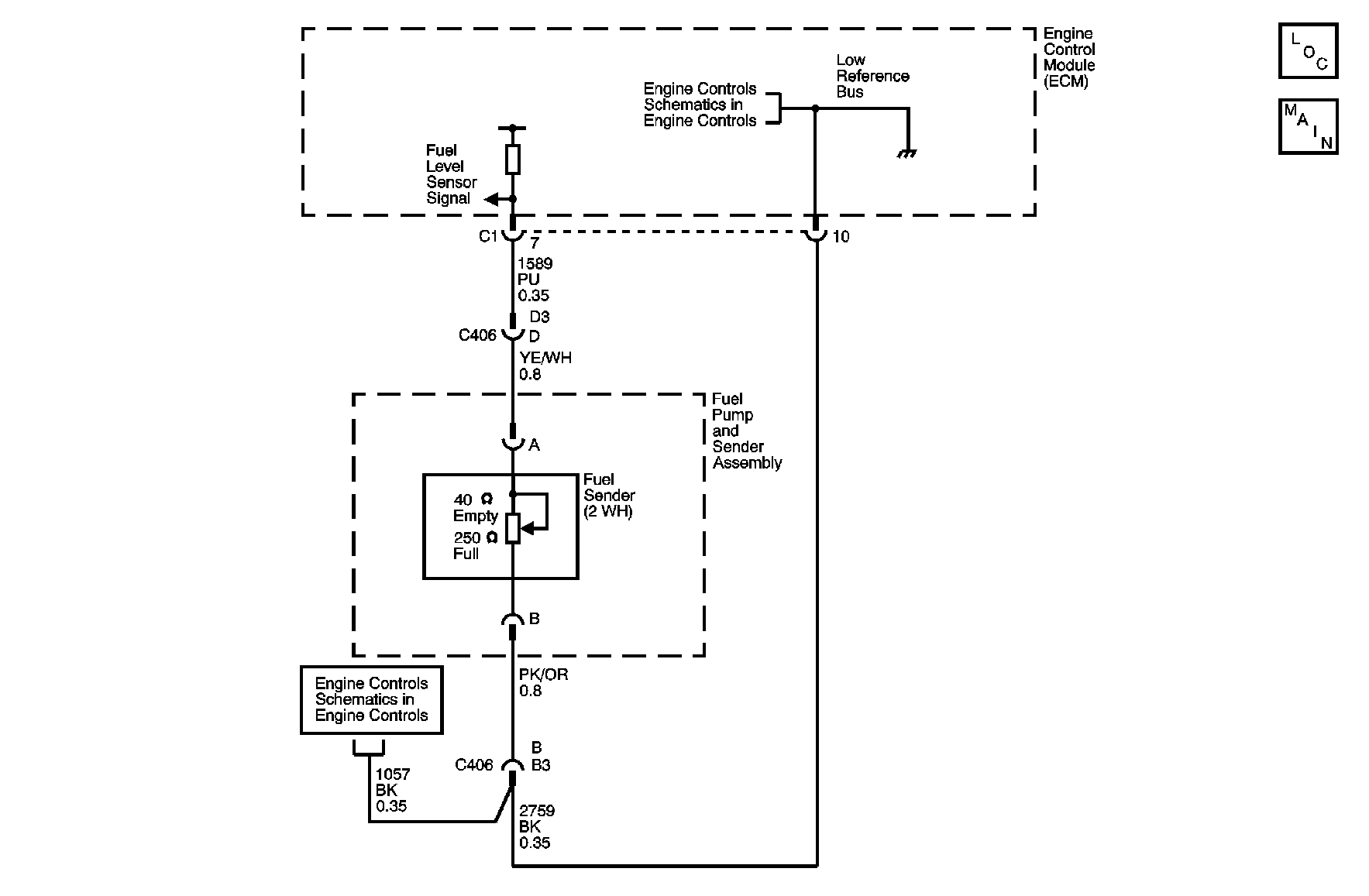
Circuit Description
The fuel level sender changes resistance based on the fuel level. The engine control module (ECM)/powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the signal circuit of the fuel level sender in order to determine fuel level. When the fuel tank is full, the sender resistance is high and the ECM/PCM senses a high signal voltage. When the fuel tank is empty, the sender resistance is low and the ECM/PCM senses a low signal voltage. The ECM/PCM uses the signal circuit of the fuel level sender in order to calculate the total remaining fuel percent in the tank. The ECM/PCM sends the fuel level percent via the class 2 serial data circuit to the body control module (BCM). The BCM sends that class 2 message to the instrument panel cluster (IPC) in order to display the fuel level percent on the fuel gage. The fuel level information is also used for misfire and evaporative emission (EVAP) diagnostics.
This diagnostic tests for a higher than normal fuel level sender signal.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The ignition is ON, with the engine ON.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The fuel level signal is greater than 98 percent. |
| • | The above condition is present for greater than 5 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The fuel gage defaults to empty. |
| • | The ECM/PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The ECM/PCM displays the failure information in the Failure Records on the scan tool. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The DTC becomes history when the conditions for setting the DTC are no longer present. |
| • | The history DTC clears after 40 malfunction free warm-up cycles. |
| • | The ECM/PCM receives the clear code command from the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Use the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data in order to locate an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in determining the number of miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also aid in determining the number of ignition cycles that the diagnostic reported a pass and/or fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions, i.e. RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Instrument Cluster Schematics | ||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check - Instrument Cluster? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Does the DMM indicate that the resistance is greater than the specified value? | 250 ohms | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 3 |
Does the DMM indicate that the voltage is greater than the specified value? | 0 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 4 | |
4 | Test the signal circuit of the fuel level sender between C406 and the engine control module (ECM)/powertrain control module (PCM) for an open, for a high resistance, or for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 5 |
5 | Test the low reference circuit of the fuel level sender between C406 and the ECM/PCM for an open or for a high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 9 |
6 | Test the signal circuit of the fuel level sender for an open, for a high resistance, or for a short to voltage between C406 and the fuel level sender. Refer to Circuit Testing and to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 7 |
7 | Test the low reference circuit of the fuel level sender for an open or for a high resistance between C406 and the fuel level sender. Refer to Circuit Testing and to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 8 |
8 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the fuel level sender. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 10 |
9 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the ECM/PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 11 |
10 | Replace the fuel level sender. Refer to Fuel Level Sensor Replacement in Engine Controls - 2.2L (L61) or to Fuel Level Sensor Replacement in Engine Controls - 2.0L (LSJ). Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 12 | -- |
11 |
Important: Program the replacement ECM/PCM. Replace the ECM/PCM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement in Engine Controls - 2.2L (L61) or to Powertrain Control Module Replacement in Engine Controls - 2.0L (LSJ). Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 12 | -- |
12 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
