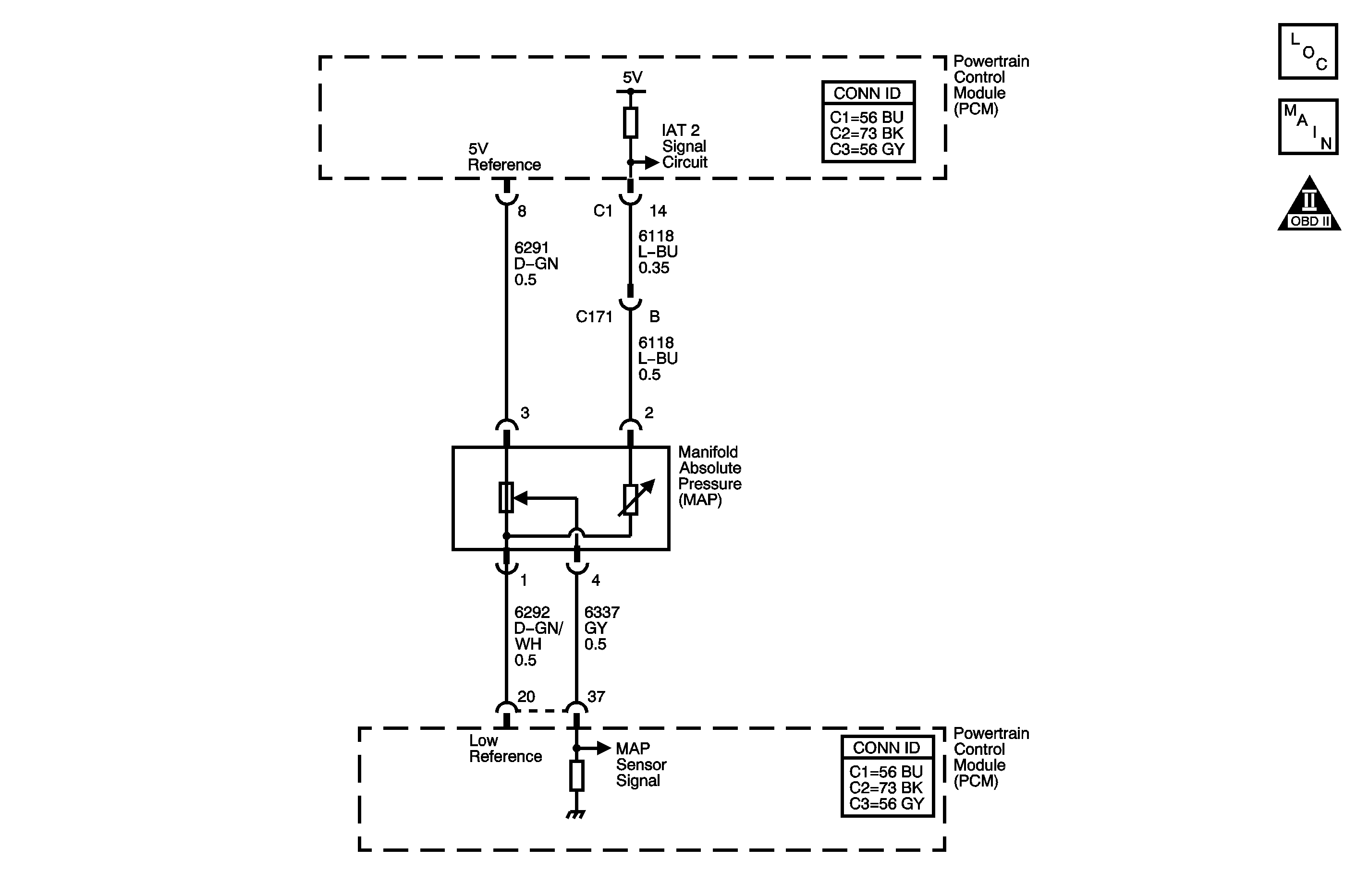
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor that resides in the engine intake manifold is integrated with the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 2. The purpose of this integrated sensor is to measure the following:
| • | The atmospheric pressure and the vacuum or the reduced pressure that exists under different operating conditions in the engine intake manifold |
| • | The supercharged air pressure that exists under high load or wide open throttle conditions in the engine intake manifold |
| • | The IAT sensor 2 after the supercharger and the intercooler as it enters the engine intake manifold |
| • | The IAT sensor 2 after the supercharger bypass valve and the intercooler as it enters the engine intake manifold |
The MAP/IAT sensor 2 has the following types of circuits:
| • | A powertrain control module (PCM) supplied and regulated MAP 5-volt reference circuit |
| • | A PCM supplied ground for the low reference circuit that is shared by the MAP and the IAT sensor 2 |
| • | A MAP sensor signal circuit that supplies a voltage input to the PCM |
| • | A PCM supplied 5-volt, IAT signal circuit |
The diaphragm within the MAP sensor responds to all of the various pressure changes in the intake manifold and provides a signal voltage to the PCM on the signal circuit relative to those pressure changes.
The PCM monitors the MAP sensor signal for voltage that is outside of the normal range of a properly operating sensor. If the PCM detects a MAP sensor signal that is not within range of a calibrated limit of the estimated value, DTC P0106 sets.
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC P0106 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Performance
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0107, P0108, P0120, P0121, P0220, P0506, P0507, P2135 are not set. |
| • | The engine speed is between 400-6,400 RPM. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is between 70-125°C (158-257°F). |
| • | The IAT is between -7 to +125°C (+19 to +257°F). |
| • | The change in throttle position (TP) is less than 5 percent. |
| • | The above enabling criteria must be stable for more than 5 seconds. |
| • | DTC P0106 runs continuously when the above conditions are met. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects that the MAP sensor signal is 25 kPa more than the calibrated estimate for more than 90 seconds.
OR
The PCM detects that the MAP sensor signal is 45 kPa less than the calibrated estimate for more than 90 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls Connector End Views or Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views | ||||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||
2 | Inspect for the following conditions:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||
3 |
Important: The following sensors share a bused low reference circuit within the powertrain control module (PCM) and a common ground. A high resistance on that shared portion will shift both sensors.
Is the difference between the MAP Sensor parameter and the BARO parameter more than the specified value? | 5 kPa | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||||
4 |
Important: The Altitude vs. Barometric Pressure table indicates a pressure range for a given altitude under normal weather conditions. Weather conditions consisting of very low or very high pressure and/or very low or very high temperature may cause a reading to be slightly out of range.
Is the MAP Sensor parameter within the specified range as indicated on the Altitude vs. Barometric Pressure table? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||
5 |
Does the MAP Sensor kPa parameter decrease? | -- | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||
6 |
Is the decrease in the MAP Sensor parameter consistent? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||
7 | Apply vacuum with the vacuum pump until 20 inch Hg is reached. Is the MAP Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 34 kPa | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||
8 | Disconnect the vacuum pump from the MAP sensor. Does the MAP Sensor parameter return to the value observed in Step 4? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||
9 | An engine in poor mechanical condition can cause this DTC to set. Inspect for the following conditions:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||
10 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the MAP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||||
11 |
Is the MAP Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 0.1 V | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||||
12 |
Is the voltage within the specified range? | 4.8-5.2 V | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 13 | ||||||||||
13 | Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 5.2 V | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 17 | ||||||||||
14 |
Important: All electrical components and accessories must be turned OFF.
Is the resistance more than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||
15 | Test the MAP sensor signal circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||
16 | Test all branches of the 5-volt reference circuit that is shared with the MAP sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||
17 | Test the 5-volt reference circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for a high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||
18 | Test the low reference circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for a high resistance or an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||
19 | Test for shorted terminals and for poor connections at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 21 | ||||||||||
20 | Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- | ||||||||||
21 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- | ||||||||||
22 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 23 | ||||||||||
23 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |||||||||||
