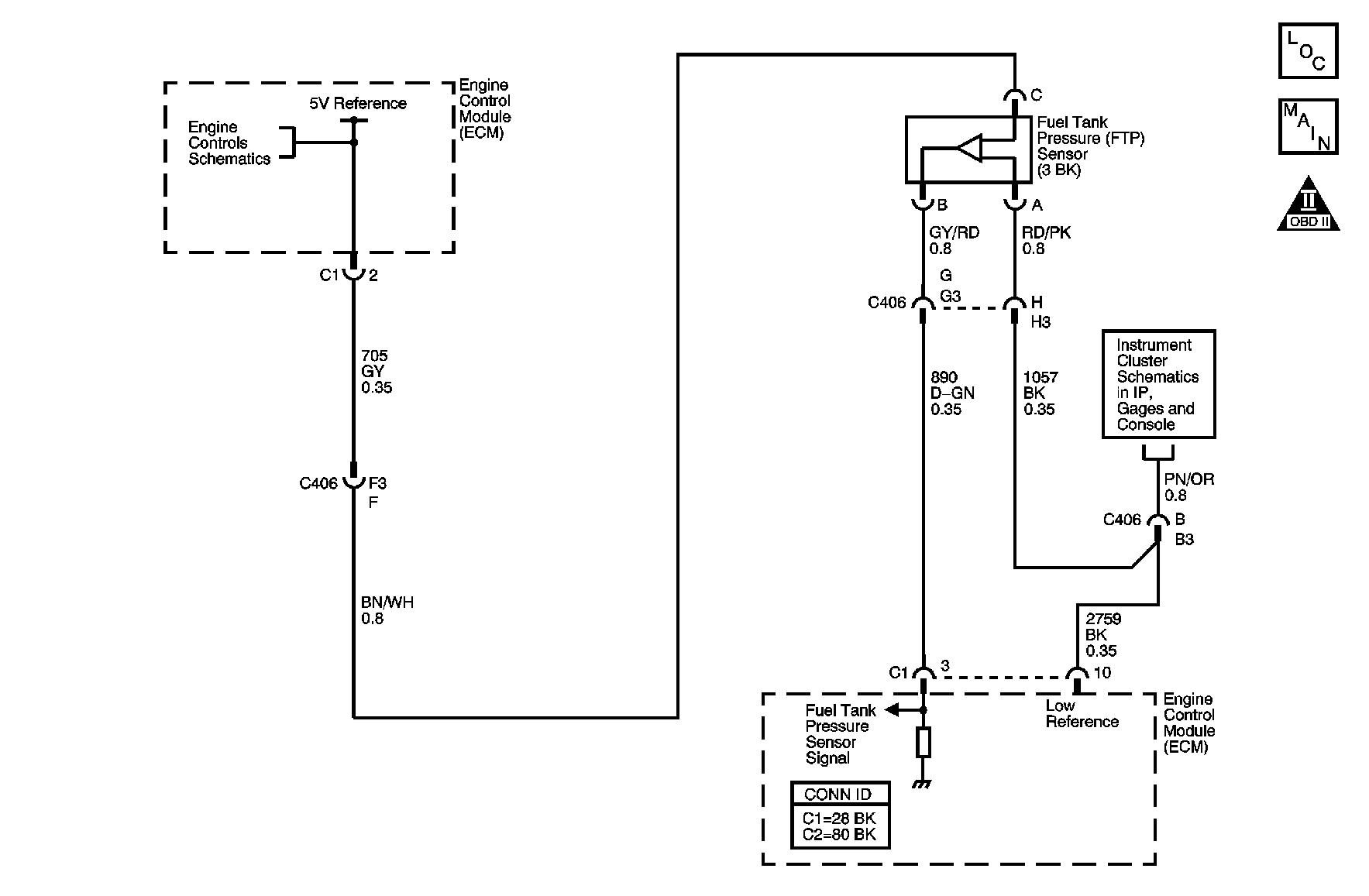
System Description
The control module tests the evaporative emission (EVAP) system for a large leak. The control module monitors the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor signal to determine the EVAP system vacuum level. When the conditions for running are met, the control module commands the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve OPEN and the EVAP vent solenoid valve CLOSED . This allows engine vacuum to enter the EVAP system. At a calibrated time, or vacuum level, the control module commands the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve closed, sealing the system, and monitors the FTP sensor input in order to determine the EVAP system vacuum level. If the system is unable to achieve the calibrated vacuum level, or the vacuum level decreases too rapidly, this DTC sets.
The following table illustrates the relationship between the ON and OFF states, and the OPEN or CLOSED states of the EVAP canister purge and vent solenoid valves.
Control Module Command | EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid Valve | EVAP Canister Vent Solenoid Valve |
|---|---|---|
ON | Open | Closed |
OFF | Closed | Open |
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0452, P0453, P0500, P0601, P0602, P0606, P0641 are not set. |
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | The ignition voltage is between 11-18 volts. |
| • | The barometric pressure (BARO) is more than 74 kPa. |
| • | The fuel level is between 15-85 percent. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is between 5-32°C (41-90°F). |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) is between 5-32°C (41-90°F). |
| • | The start-up ECT and IAT are within 9°C (16°F) of each other. |
| • | No vehicle speed DTCs are set in the transmission control module (TCM). |
| • | The engine run time is less than 10 minutes. |
| • | Accumulated purge mass is more than 6000 grams. |
Conditions For Setting the DTC
The EVAP system is not able to achieve or maintain vacuum during the diagnostic test.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | To help locate intermittent leaks, use the J 41413-200 (J 41413-100) Evaporative Emissions System Tester (EEST) to introduce smoke into the EVAP system. Move all EVAP components while observing smoke with the High Intensity White Light. |
| • | Introducing smoke in 15 second intervals may allow smaller leaks to be more noticeable. When the system is less pressurized, the smoke will sometimes escape in a more condensed manner. |
| • | A temporary blockage in the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve, purge pipe or EVAP canister could cause an intermittent condition. Inspect and repair any restriction in the EVAP system. |
| • | To improve the visibility of the smoke exiting the EVAP system, observe the suspected leak area from different angles with a High Intensity White Light. |
| • | An FTP sensor that does not correctly respond to vacuum, or pressure may cause this DTC to set. |
| • | Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition. |
| • | For intermittent conditions refer to Intermittent Conditions . |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics and Evaporative Emissions Hose Routing Diagram Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls Connector End Views | ||||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||
2 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||
3 |
Does the EVAP canister vent solenoid valve operate when it is commanded ON and OFF? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||||
4 |
Important: Ensure that the vehicle underbody temperature is similar to the ambient temperature, and allow the surrounding air to stabilize before starting the diagnostic procedure. System flow will be less with higher temperatures.
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||||
Is the difference between the scan tool Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter and the pressure/vacuum gage on the J 41413-200 (J 41413-100) within the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 12 | |||||||||||
7 |
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter more than the second specified value? | 10 in H2O 5 in H2O | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 12 | ||||||||||
8 |
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 9 | ||||||||||
9 | Disconnect the EVAP purge vacuum source from the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve. Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||
10 | Disconnect the EVAP purge pipe from the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve. Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||||
11 | Disconnect the EVAP purge pipe at the EVAP canister. Is the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 1 in H2O | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 17 | ||||||||||
12 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||||
13 | Repair the pinched or obstructed EVAP purge solenoid vacuum source. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
14 | Repair the restriction in the EVAP purge pipe. Refer to Evaporative Emission System Cleaning . Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
15 | Replace the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
16 | Replace the EVAP canister vent solenoid valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Vent Solenoid Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
17 | Replace the EVAP canister. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
18 | Replace the FTP sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||||
19 |
Important: Larger volume fuel tanks and/or those with lower fuel levels may require several minutes for the floating indicator to stabilize.
Is the floating indicator below the red flag? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||
20 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |||||||||||
