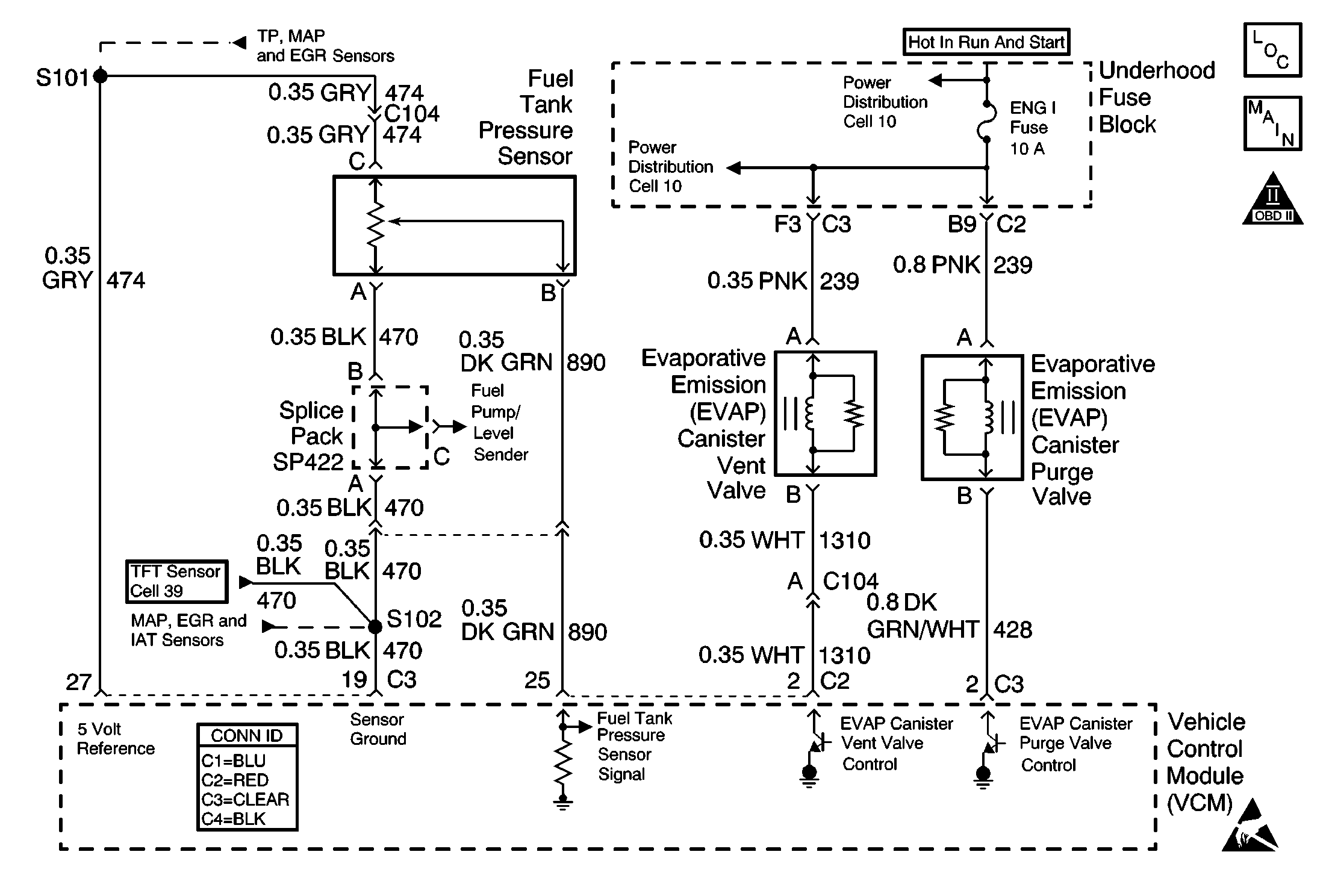
Circuit Description
The VCM monitors the performance of the evaporative emissions (EVAP) system by applying a predetermined level of vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring the vacuum decay rate. The VCM sets this DTC if the vacuum decay rate is more than a predetermined value. The VCM monitors the amount of vacuum and the amount of pressure in the EVAP system by monitoring the fuel tank pressure sensor. For this DTC, the VCM turns ON both the EVAP purge valve and the EVAP vent valve when the conditions for running the DTC are met. This applies an engine vacuum to a closed EVAP system. The VCM turns OFF both the EVAP purge valve and the EVAP vent valve when the system reaches a correct amount of vacuum. The EVAP system should quickly release the vacuum in the EVAP system with the EVAP purge valve OFF and the EVAP vent valve OFF, or open. This test indicates a blocked or restricted EVAP vent path, if the EVAP system fails to release the vacuum quickly enough.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No MAP sensor DTCs are active. |
| • | No TP sensor DTCs are active. |
| • | No VS sensor DTCs are active. |
| • | No O2 sensor DTCs are active. |
| • | No ECT sensor DTCs are active. |
| • | No IAT sensor DTCs are active. |
| • | DTC P0125 is not active. |
| • | The fuel level is more that 12.5 percent but less than 87 percent. |
| • | The system voltage is between 10 and 17 volts. |
| • | The ECT is between 4°C and 30°C (39°F to 86°F). |
| • | The IAT is between 4°C and 30°C (39°F to 86°F). |
| • | The cold start temperature difference, defined as the ECT minus the IAT, is less than: |
| 1.5°C when the IAT is more than the ECT, or |
| 8°C when the ECT is more than the IAT . |
| • | The BARO is more than 72 kPa. |
| • | The change in fuel tank vacuum is less than 0.6 inch of Hg, or the change in fuel level is less than 8 percent |
| • | The fuel tank vacuum level remains above a calibrated value for a specified number of seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The VCM fails to detect a drop in the EVAP system vacuum during a calibrated number of seconds with the vent solenoid open.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The VCM illuminates the MIL during the first key cycle in which the DTC sets. |
| • | The VCM stores the conditions that were present when the DTC sets as a Freeze Frame and Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: An accurate indication of fuel level is required for the VCM to properly pass or fail this DTC. Always diagnose fuel level sensor DTCs before performing this DTCs diagnostic table. Always check for fuel level sensor DTCs stored in history.
Check for:
| • | A loose, missing, damaged, incorrect, or improperly-installed fuel cap |
| • | Missing or damaged O-rings at the EVAP canister fuel vapor and purge line fittings |
| • | A cracked or punctured EVAP canister |
| • | Incorrectly routed or damaged EVAP system purge and vapor lines |
| • | A damaged or disconnected EVAP purge line, vent hose, or fuel tank vapor line |
| • | A stuck closed EVAP vent valve |
| • | A restricted or stuck closed fuel tank rollover valve |
| • | A poor connection at the VCM-Inspect the harness connectors for: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Faulty terminal to wire connections |
| • | A damaged harness-Inspect the wiring harness to the EVAP vent solenoid, the EVAP purge solenoid, and the fuel tank pressure sensor for an intermittent, an open circuit, or a short circuit |
| • | A kinked, pinched or plugged EVAP purge or fuel tank vapor line-Verify that the lines are not restricted |
Refer to Evaporative Emission System Cleaning before starting repairs.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If the vacuum stored in the EVAP system is quickly released, then an intermittent system restriction or failure of the EVAP vent valve or the EVAP fuel tank pressure sensor may have occurred.
-
Check the vapor canister and the EVAP vent valve for restrictions.
-
An EVAP pressure sensor that does not correctly respond to pressure or vacuum will cause this DTC to set. The EVAP pressure sensor monitors a range from 7.5 inches Hg of pressure to -17.5 inches Hg of vacuum. In order to test the EVAP pressure sensor for pressure response, seal the system with the scan tool and use the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic cart in order to apply pressure to the system. Using inches Hg, compare the pressure gauge reading on the diagnostic cart to the EVAP pressure sensor reading on the scan tool.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 | Inspect the EVAP system for:
Repair the EVAP system if needed. Did you make a repair to the EVAP system? | -- | ||
3 | Are DTCs P0452 or P0453 also set? | -- | ||
Does the EVAP fuel tank pressure sensor quickly drop to near 0 in Hg when 0 percent EVAP purge is commanded and the EVAP vent valve is opened? | -8 in Hg | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Does the vacuum drop from the specified value when the EVAP vent valve is opened? | 5 in Hg | |||
6 |
Does the vacuum drop from the specified value when the vent line is unplugged? | 5 in Hg | ||
7 |
Did you replace the EVAP vent line? | -- | ||
8 |
Was the fuel tank vapor line replaced? | -- | ||
|
Important: The following steps require the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station J 41413 . Using in Hg, always zero the EVAP pressure and vacuum gauges on the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station before proceeding with diagnosis.
Do both values indicate the same vacuum in the EVAP system to within the range specified? | + / - 2 in H2O | |||
10 |
| -- | ||
11 | Check for a short to ground on the EVAP vent valve driver circuit. Repair the circuit as necessary. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
12 | Replace the EVAP vent valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Vent Valve Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Replace the EVAP vapor canister. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Replace the EVAP fuel tank pressure sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
15 |
Important: The replacement VCM must be programmed. Replace the VCM. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | ||
16 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | -- | |
17 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to applicable DTC | System OK |
