Important: A condition that may cause the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) to illuminate may not store a diagnostic trouble code (DTC). DO NOT use the DTC tables for intermittent concerns. The fault must be present in order to correctly diagnose the concern.
Intermittent concerns are most often caused by faulty electrical connections or faulty wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical check for the following conditions:| • | Faulty mating of the electrical connector halves or a terminal(s) that is not fully seated in the connector body (backed out). |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminal(s). |
| • | Reduced physical tension between the electrical terminals in the circuit connections. Reform or replace any faulty or suspect electrical terminals in order to insure proper contact tension. |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connection. Remove the terminal from the connector body in order to check the crimp and/or solder to the wire conductor. |
Road test the vehicle with a J 39200 Digital Multimeter or an equivalent connected to the suspected circuit. Look for an abnormal voltage when the malfunction occurs. An abnormal reading on the multimeter display is an indication that there may be a malfunction in the circuit that was being monitored.
Use a scan tool in order to detect intermittent conditions. The GM Techline equipment scan tools have several features that can locate an intermittent condition. Use the following features in order to find intermittent faults:
| • | The Snapshot feature can capture and store engine parameters within the scan tool when the malfunction occurs. The stored information can be reviewed by the service technician in order to see what caused the malfunction. |
| • | The Freeze Frame buffer or the Failure Records buffer are valuable tools in locating an intermittent condition. Review and capture the information in the Freeze Frame or Failure Record associated with the intermittent DTC that is being diagnosed. Drive the vehicle in the conditions that were present when the DTC was originally set. |
Check for a loss of DTC memory. A customer concern of an malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) that comes ON but has no stored DTCs can be checked with the following steps:
- Disconnect the TP sensor and idle the engine until the MIL illuminates (engine speed may have to be increased to 2,000 RPM in order to set the DTC).
- Check that a DTC P0122 is stored and kept in the PCM memory when the ignition is OFF.
- The PCM or the memory power input circuit is faulty if a DTC P0122 is not stored in the PCM memory.
- Clear the DTC P0122.
An intermittent malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) with no stored DTC may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | Secondary ignition voltage that is shorting to ground and arcing at the ignition wires, the ignition coil, or the spark plugs. |
| • | Faulty PCM grounds. Refer to
Cell 20: Power and Ground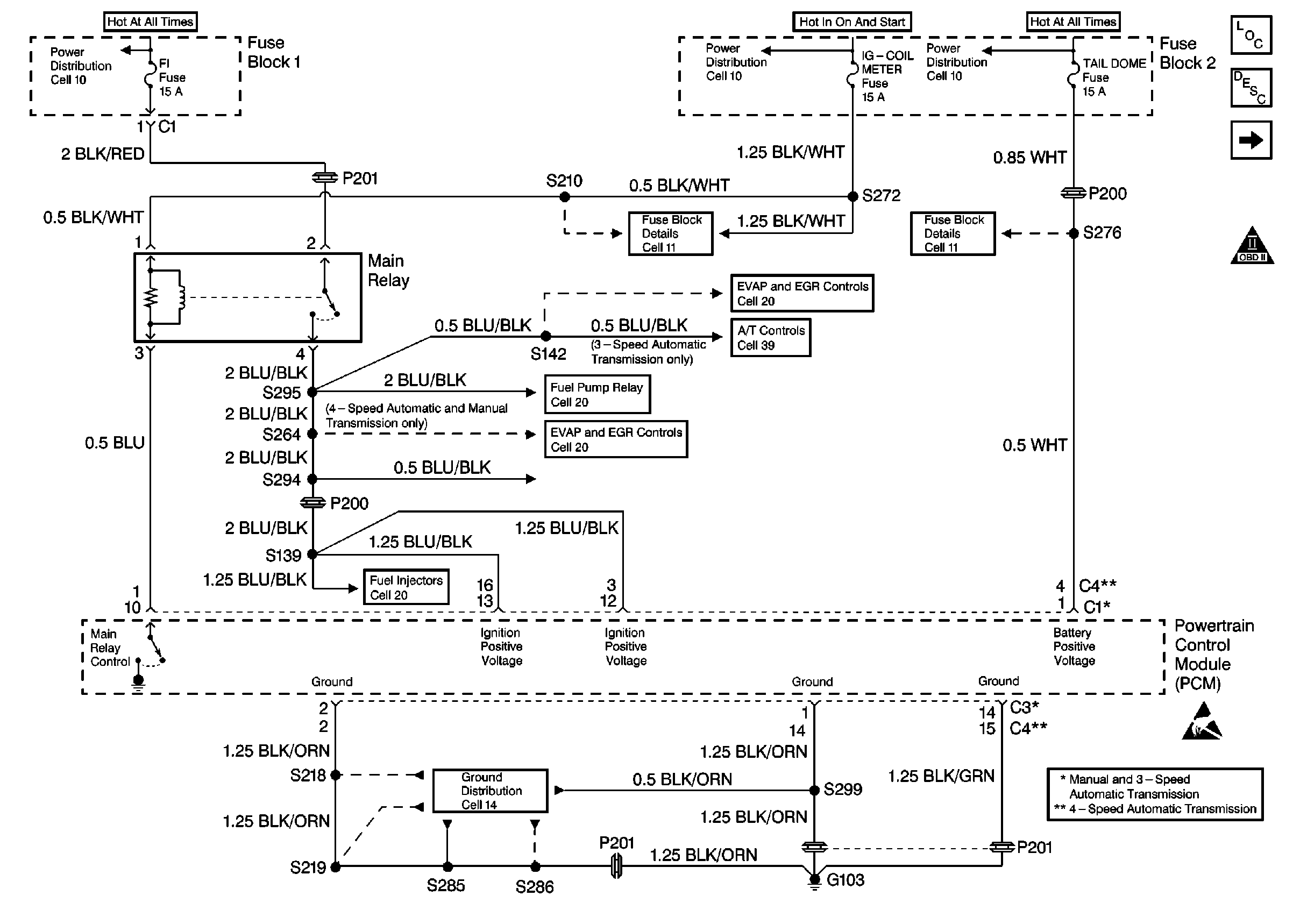
. |
An intermittent start and stall concern may be related to a malfunction in the theft deterrent system. Check for any theft deterrent DTC(s). Check for the improper installation of electrical accessories such as lights, cellular phones, etc.
All ignition control (IC) wires should be routed away from any secondary ignition wires, the distributor, the ignition coil, and the generator. All wires from the PCM to distributor should have a good connection. The PCM and the distributor (or IC module) should have good electrical grounds.
