DTC 69 TCC Stuck ON L57 MFI
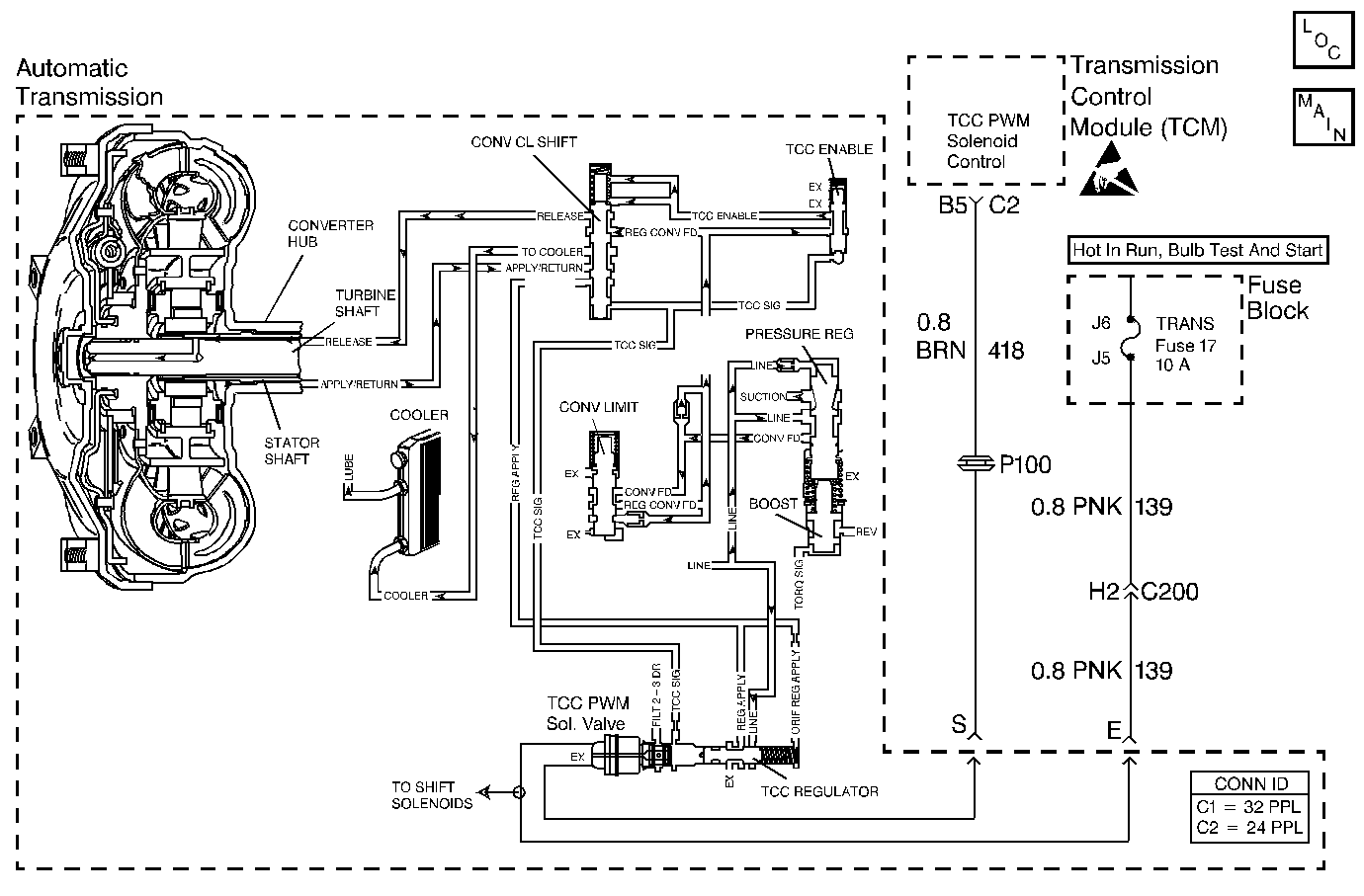
Circuit Description
The transmission control module (TCM) energizes the torque converter clutch pulse width modulated (TCC PWM) solenoid valve by grounding circuit 418. This blocks the exhaust for TCC signal fluid and allows filtered 23 drive fluid to feed the TCC signal circuit. When the vehicle's operating conditions are appropriate for TCC application, the TCM begins the TCC duty cycle to approximately 30%. This allows TCC signal fluid pressure to move the converter clutch shift valve into the apply position and direct regulated apply fluid to the torque converter. The TCM then increases (ramps) the duty cycle to approximately 60%, where regulated apply fluid pressure applies the converter clutch. The vehicle application determines the TCC apply rate. Once the TCC applies, the duty cycle immediately increases to approximately 70% to achieve full apply pressure in the regulated apply fluid circuit.
The TCC PWM solenoid valve is de-energized by the TCM opening circuit 418. This action allows the TCC signal fluid to exhaust through the solenoid and blocks filtered 23 drive fluid from entering the TCC signal circuit. The loss of fluid pressure in the TCC signal circuit releases the TCC.
If the TCM detects high TCC slip when the TCC is commanded ON, then DTC 69 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The following conditions occur once per TCC cycle two consecutive times:
| • | No TP sensor DTC 21 or DTC 22. |
| • | No TFP manual valve position switch DTC 28. |
| • | No A/T ISS sensor DTC 74. |
| • | No camshaft position sensor (CMP). |
| • | Transmission range is D3 or D4. |
| • | The commanded gear indicates 2nd or 3rd. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The TCC slip speed must be -5 to +10 RPM for at least 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The TCM does not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The TCM stores DTC 69 in TCM history. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A scan tool clears the DTC from TCM history. |
| • | The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive key cycles without a diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The TCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is OFF long enough in order to power down the TCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the TCC is mechanically stuck ON, with the parking brake applied and any gear range selected, the TCC fluid mechanically applies the TCC. TCC fluid mechanically applying the TCC can cause an engine stall. |
| • | A stuck or skewed TP sensor may set DTC 69. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step tests the mechanical state of the TCC. When the TCM commands the TCC solenoid OFF, the slip speed should increase.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Important:: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Failure Records from the TCM. Are the TP angle values within the specified range? | 0% at Closed Throttle 100% at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Drive the vehicle in D4, under steady acceleration, with a TP angle greater than 15%. Does the Scan Tool display a TCC slip speed of -5 to 10 RPM, while the displayed TCC duty cycle is 0%? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
4 | The TCC is mechanically stuck ON. Perform the following inspections:
Refer to Symptom Diagnosis TCC Stuck-On. Was the condition corrected? | -- | -- | |
5 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Does the Scan Tool indicate greater than 10 RPM for 4 seconds? | -- | System OK |
