| Table 1: | EGR Valve Terminal (Pin) Identification |
Circuit Description
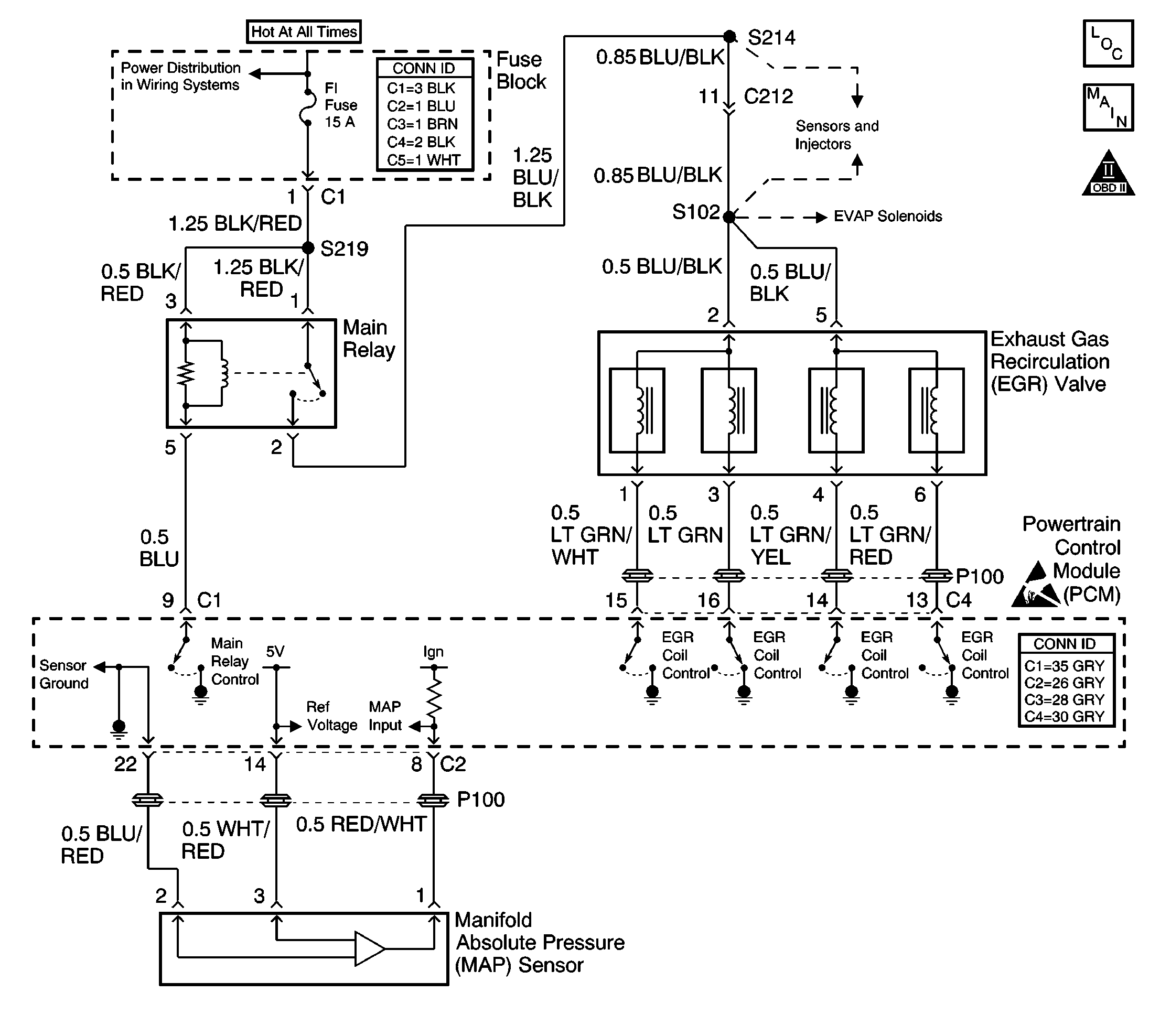
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system controls the formation of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions by recirculating the exhaust gases into the combustion chamber. The powertrain control module (PCM) uses the expected changes in the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor readings in order to evaluate the performance of the EGR system. The PCM sends a signal to the EGR valve while monitoring the MAP sensor signal. The PCM suspects that the EGR valve flow is incorrect when the monitored MAP sensor pressure change is too small.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The barometric pressure (BARO) is more than or equal to 75 kPa. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature is between 70°C and +110°C (158°F-230°F). |
| • | The intake air temperature is more than -8°C (+18°F). |
| • | Vehicle speed is at least 97 k/hr (60 mph) for 5 minutes prior to deceleration. |
| • | During deceleration the throttle valve angle is 0 degrees and the engine is operating in Fuel Cutoff mode. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The difference in intake manifold pressure between when the EGR valve is OPEN, and when the EGR valve is CLOSED, is less than a specified value.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 2 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information is stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns off after 3 consecutively passing trips without a fault present. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Perform the scan tool Clear DTC Information function in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
A DTC P0400 is more likely to set during a combination of highway and city driving. Operate the vehicle in stop-and-go situations with short trips on the highway in order to validate DTC P0400.
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | An EGR valve that is stuck closed, stuck open, or binding. |
| • | The incorrect PCM can cause DTC P0400 to set. Check that the correct PCM is installed in the vehicle as required for proper emission certification. |
A DTC P0400 may set when the expected change in MAP is more than or less than the expected value during the operation of the EGR valve. Investigate any condition that can affect the accuracy of the MAP sensor readings:
| • | A retarded ignition timing |
| • | A restricted exhaust system |
| • | A faulty MAP sensor |
| • | A restriction or a leak that affects the flow of exhaust gases through the EGR valve and into the intake air system. |
If a DTC P0400 is intermittent, driving the vehicle under the following conditions can verify whether the fault is present. Perform the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. Road test the vehicle while monitoring the DTC P0400 diagnostic on the scan tool under the Not Ran Since Code Cleared selection in the DTC Information menu. If a DTC P0400 appears in the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list, the P0400 diagnostic has not yet run. When the DTC P0400 does not appear in the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list, the P0400 diagnostic has run. If the MIL is NOT illuminated, and there is no Pending DTC Status in DTC Information, the P0400 diagnostic has passed. The DTCs MUST be cleared in order to view the Current Status of the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list. DO NOT forget that the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list only indicates that the test has run, not whether the test passed or failed. The DTC Information screen must be checked for Current or Pending status in order to determine the outcome of the diagnostic test involved.
If a DTC P0400 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining the vehicle operating conditions when the DTC was first set.
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the EGR control system electrical circuits. Check for the following conditions:
| • | Any backed-out terminals |
| • | Any improper mating of terminals |
| • | Any broken electrical connector locks |
| • | Any improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Any faulty terminal-to-wire connections |
| • | Any physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Any corrosion of the electrical connections, the splices, or the terminals |
Use the following table in order to locate the correct terminals to test during diagnosis. The table layout corresponds to the pin location of the EGR valve electrical terminals.
Connector Lock Tab | ||
Pin 3 | Pin 2 | Pin 1 |
Pin 6 | Pin 5 | Pin 4 |
Test Description
The number below refer to the step number in the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step checks for an EGR valve that is leaking, stuck open, or turned on at idle. Normal engine operating temperature is specified as 80°C (176°F) or above.
-
This step checks the operation of the EGR valve. The duty cycle output control of the EGR is disabled by the PCM when any DTCs are stored and when the engine temperature is less than 80°C (176°F).
-
This step checks for a physically stuck EGR valve or plugged EGR passages.
-
This step checks the ignition positive voltage supply to the EGR coils.
-
This step checks for proper manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor operation. The diagnostic for a DTC P0400 depends on MAP sensor output in order to monitor EGR valve performance.
-
Fault not present indicates the condition that caused DTC P0400 to set is intermittent and not currently present. If no other DTCs are stored, refer to Diagnostic Aids for additional information on diagnosing an intermittent DTC P0400.
-
This step determines whether an electrical fault is the cause of the EGR valve staying open. A grounded EGR valve control circuit can cause the EGR valve to be open all the time.
-
This step checks for an EGR valve control circuit that is shorted to ground. If the circuit wiring is OK, a faulty PCM with an internally shorted circuit can cause the EGR valve to be open.
-
This step checks whether the malfunction that caused the DTC P0400 is still present. Driving the vehicle under these conditions will verify whether the fault is present. After performing the scan tool Clear DTC Information function, the DTC P0400 diagnostic can be monitored on the scan tool under the Not Ran Since Code Cleared selection in the DTC Information menu. If DTC P0400 appears in the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list, the P0400 diagnostic has not yet run. When DTC P0400 does not appear in the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list, the P0400 diagnostic has run. If the MIL is NOT illuminated and there is no Pending DTC Status in DTC Information, the P0400 diagnostic has passed. The DTCs MUST be cleared in order to view the Current Status of the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list. DO NOT forget that the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list only indicates that the test has run, not whether the test passed or failed. The DTC Information screen must be checked for Current or Pending status in order to determine the outcome of the diagnostic test involved.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||
2 | Is DTC P0403 also set? | -- | Go to DTC P0403 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid Control Circuit | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||
Does the engine run rough, or is the idle unstable? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||
Does the engine run rough or stall? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||
5 |
Does the EGR valve pass both tests? | 5% | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||
6 |
Does the EGR valve pass both tests? | 5% | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||
7 |
Does the EGR valve pass all resistance tests? | 20-24 ohms at 20°C (68°F) | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 17 | ||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 17 | |||||||||
Did the test lamp illuminate for both circuits? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 15 | |||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||
The fault is not present. Are there any DTCs stored that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||
With the engine running, disconnect the EGR valve electrical connector. Does the engine performance improve when the EGR valve is disconnected? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 13 | |||||||||
13 |
Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 18 | |||||||||
15 | Repair the ignition positive voltage supply to the EGR valve. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||
16 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||
17 | Replace the EGR valve. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||
18 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- | ||||||||
Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool? | -- | System OK |
