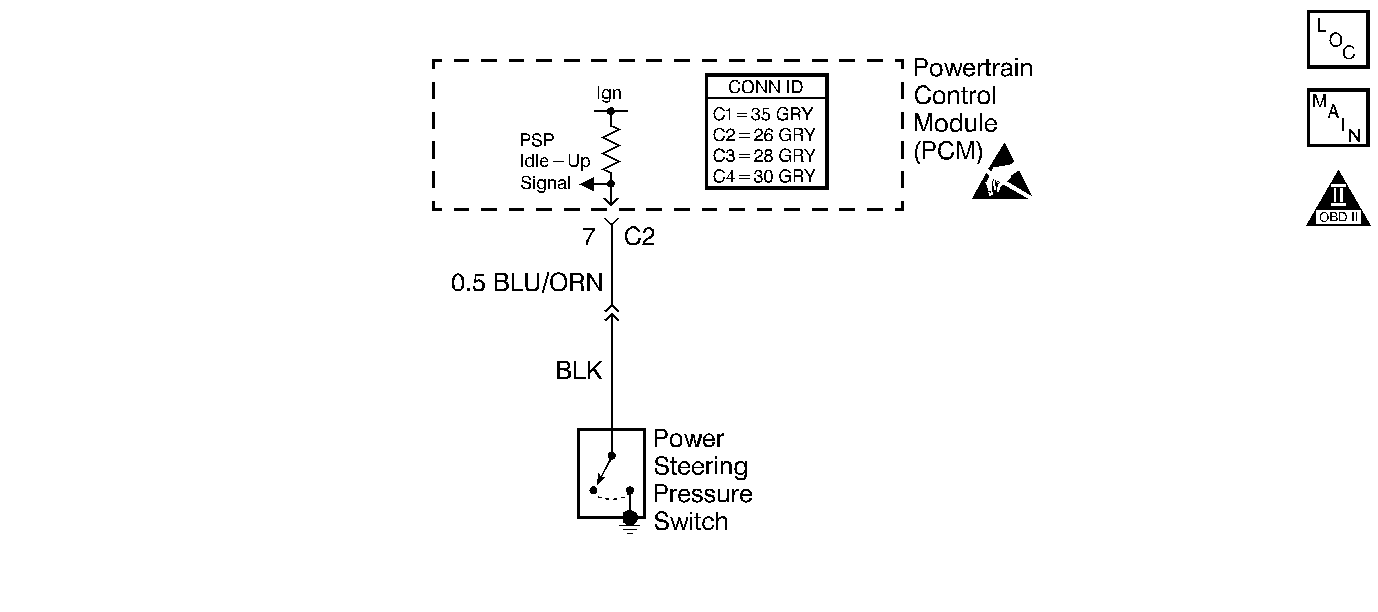
Circuit Description
The power steering pressure (PSP) switch is a normally open switch. During normal straight ahead driving conditions the PSP switch signal is closed to battery voltage. When the steering wheel is turned, causing power steering pressure to increase, the PSP switch closes, pulling the switch voltage to ground. The PCM increases the idle speed in order to prevent diminished engine idle quality or engine stalling, in response to a low PSP switch signal.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | A PSP switch that is shorted can cause the engine idle speed to remain high even when driving straight ahead. |
| • | A PSP switch that is incorrectly calibrated can cause the engine idle speed to remain low when steering pump hydraulic pressure is high. |
| • | A faulty ground in the PSP switch can cause erratic switch operation. Inspect that the PS pump and bracket are secure, insuring a good path to ground. Inspect the PSP switch for a tight installation. |
| • | A PS pump delivering low pressure. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step checks for voltage from the PCM or for an open or a short to ground in the PSP switch signal circuit.
-
This step checks for an inadequate ground connection at the power steering pump or a faulty PSP switch.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check? | -- | ||
2 |
Did the scan tool indicate ON when the steering wheel was turned all the way in either direction? | -- | Go to Symptoms | |
3 |
Was the voltage near the specified value? | B+ | ||
4 |
Was the test lamp ON when the steering wheel was turned all the way to the right or left? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
5 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
6 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
7 | Replace the PSP switch. Refer to PSP Switch Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Operate the vehicle within the conditions under which the original symptom was noticed. Does the system now operate properly? | -- | System OK | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
