Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
Indicators
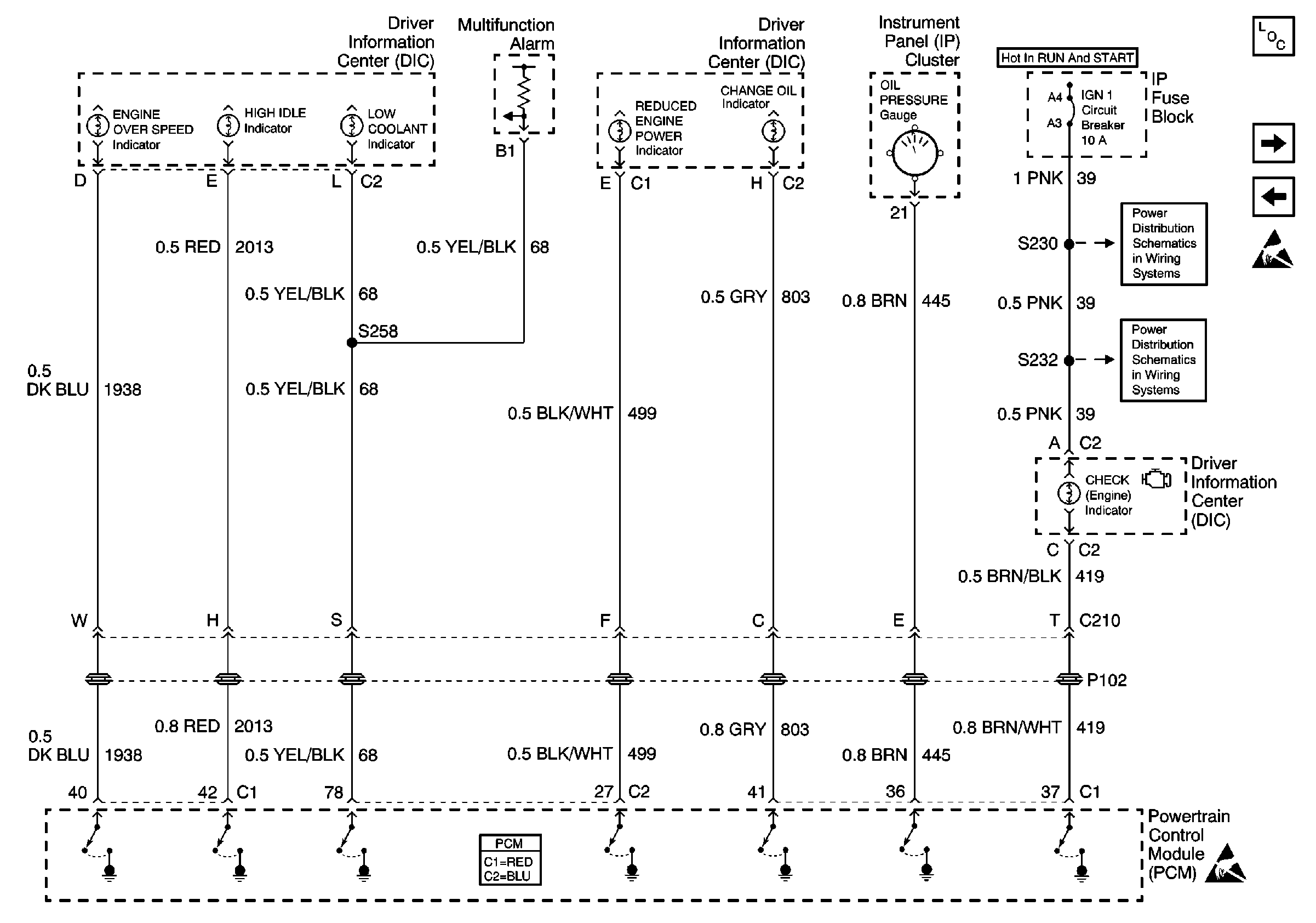
.
Circuit Description
The engine oil pressure gauge supplies ignition positive voltage to the PCM by way of the engine oil pressure gauge control circuit. The engine oil pressure signal is sent to the PCM from the engine oil pressure sensor. The PCM controls the engine oil pressure gauge by momentarily grounding the engine oil pressure gauge control circuit and causing the voltage to pulse. The solid state circuits of the engine oil pressure gauge convert the voltage pulses in order to drive the gauge pointer and display engine oil pressure in Pounds per Square Inch (PSI).
The PCM monitors the voltage on the Engine Oil Pressure gauge control circuit in order to determine if the circuit is open or shorted to ground.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine speed is at least 600 RPM.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The Engine Oil Pressure gauge control circuit voltage is less than 0.48 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | A last test failed (Current DTC) will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at the PCM or instrument cluster. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect the PCM, turn the ignition ON and observe a voltmeter connected to the engine oil pressure gauge control circuit at the PCM harness connector while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the engine oil pressure gauge control circuit. A change in voltage will indicate the location of the fault. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool indicate that the EOP Sensor parameter is greater than the specified value? | 0.48 volt | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||
4 | Test the engine oil pressure gauge control circuit for an open. Refer to Testing for Continuity in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
5 | Test the engine oil pressure gauge control circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Testing for Short to Ground in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
6 | Inspect for poor connections at the I/P cluster connector. Refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
7 | Inspect for poor connections at the PCM connector. Refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
8 | Replace the I/P cluster. Refer to Instrument Cluster Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Important:: Program the new PCM. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
11 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
