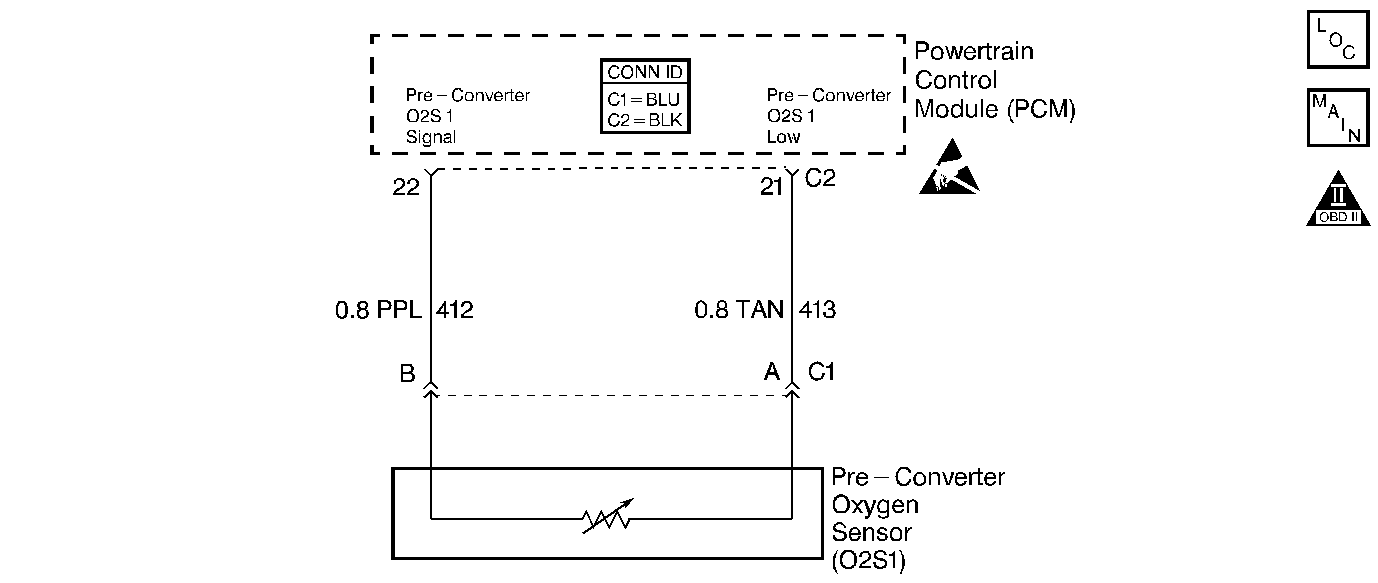
Circuit Description
The PCM continuously monitors the Oxygen Sensor (O2S 1) activity for 100 seconds. During the monitor period, the PCM counts the number of times that the O2S 1 switches from rich to lean and from lean to rich and adds the amount of time that the O2S 1 took in order to complete all of the switches. With this information, you can determine an average time for all of the switches. If the average time to switch is too slow, a DTC P0133 will set.
Replace the entire oxygen sensor (O2S 1) assembly (Do not attempt to repair the oxygen sensor) if the following conditions exist:
| • | Damaged wiring |
| • | Damaged electrical connector |
| • | Damaged terminal(s) |
Conditions For Running The DTC
| • | DTCs P0105, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0171, P0201, P0202,P0203,P0204,P0300, P0335, P0440, P0442, P0446, P0506, P0507, P0601, P0602, or P1441 not set. |
| • | ECT is more than 75°C (167°F). |
| • | Engine speed is between 1800 RPM and 2300 RPM. |
| • | Engine is operating in closed loop. |
| • | Throttle Position (TP) angle is between 8 percent and 15 percent. |
| • | Evaporative emissions control system is commanded open for more than 80 percent. |
| • | Purge learned memory is more than approximately 0.86. |
| • | Diagnostic completes when 30 seconds accumulated time has been spent in the above conditions. |
Conditions For Setting The DTC
The average O2S 1 response times are more than 249 mS for rich to lean sweeps or 249 mS for lean to rich sweeps.
Or
Ratio of response times is more than 6.0 or less than 0.2.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0133 or slow response is most likely caused by one of the following items:
| • | Fuel pressure--The system will go rich if fuel pressure is to high. The PCM can compensate for some increase, however, if it gets too high, a DTC P0172 may set. Refer to the DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich 2.4L. |
| • | Leaking injector--A leaking or malfunctioning injector can cause the system to go rich. |
| • | MAP sensor--An output that causes the PCM to sense a higher than normal manifold pressure (low vacuum) can cause the system to go rich. Disconnecting the MAP sensor will allow the PCM to set a fixed value for the MAP sensor. Substitute a different MAP sensor if the rich condition is gone while the MAP sensor is disconnected. |
| • | Pressure regulator--Check for a leaking fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking for the presence of liquid fuel in the vacuum line to the fuel pressure regulator. |
| • | TP sensor--An intermittent TP sensor output can cause the system to go rich due to a false indication of the engine accelerating. |
| • | O2S 1 contamination--Inspect the O2S 1 for silicone contamination from fuel or the use of improper RTV sealant. The O2S 1 sensor may have a white powdery coating and result in a high but false voltage signal (rich exhaust indication). The PCM will then reduce the amount of fuel delivered to the engine causing a severe surge or driveability problem. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
When the system is operating correctly the HO2S voltage should toggle above and below the specified values.
-
The specified value is what is measured on a correctly operating system.
-
The specified value is what is measured on a correctly operating system.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
|
Important: If any other DTCs are set, except HO2S DTCs, refer to other DTCs first before proceeding with this table.
Does scan tool indicate O2 voltage varying outside the specified values? | 400-500 mV | |||||||||
3 | Operate vehicle within Fail Records conditions. Does the scan tool indicate this DTC failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||
4 | Inspect and test for the following:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? | 450 mV | |||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate O2 voltage at or near the specified value? | 0 mV | |||||||||
7 | Test the low circuit for an open or high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
8 | Test the signal circuit for an open or high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
9 | Test for poor connections at the HO2S. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
10 |
Important: Determine the cause of contamination before replacing the sensor. Inspect and test for the following:
Replace the effected O2 sensor. Refer to Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||
11 | Test for poor connections at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
|
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Replace the PCM. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | ||||||||
13 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | ||||||||
14 | Use the scan tool in order to check for DTCs. Does the scan tool indicate any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | System OK |
