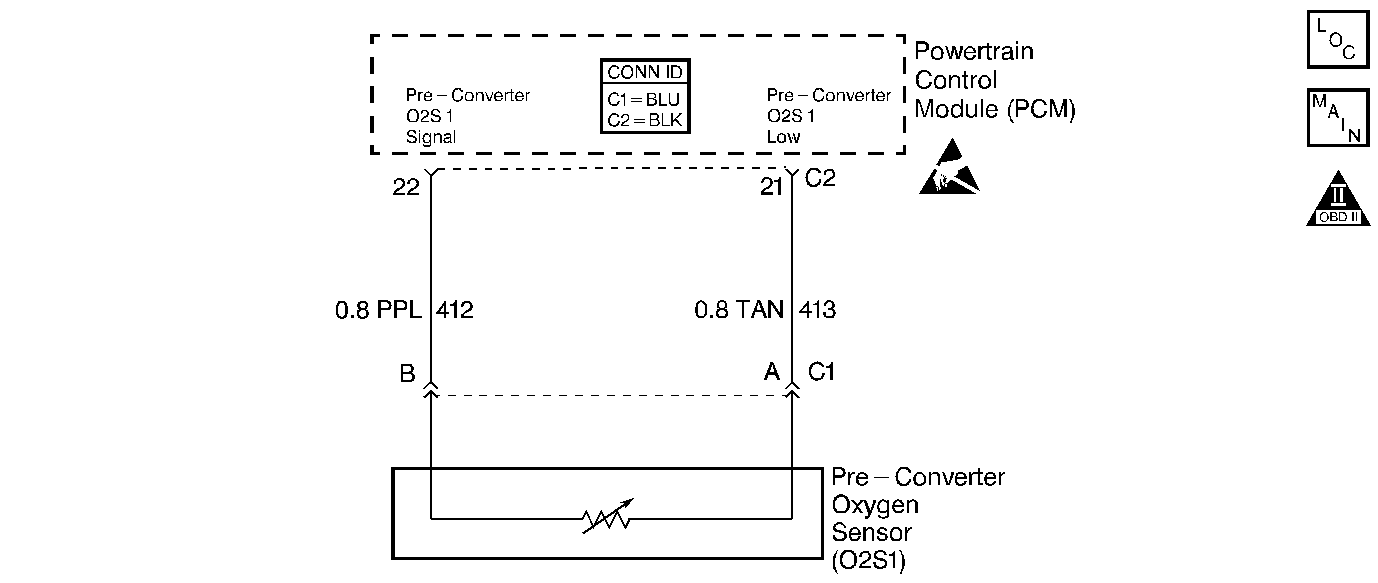
Circuit Description
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) supplies a voltage of approximately 0.45 volt between the oxygen sensor (O2S 1) signal and the ground circuit. The oxygen sensor (O2S 1) varies the voltage within a range of approximately 1 volt if the exhaust is rich, to approximately 0.10 volt if the exhaust is lean.
The sensor is like an open circuit and produces no voltage when the temperature is less than 315°C (600°F). An open sensor circuit or a cold sensor causes an open loop operation.
Replace the entire oxygen sensor (O2S 1) assembly. Do not attempt to repair the oxygen sensor if the following conditions exist:
| • | Damaged wiring |
| • | Damaged electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
Conditions For Running The DTC
| • | DTCs P0105, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0171, P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0300, P0335, P0440.P0442, P0446, P0506, P0507, P0601, P0602, or P1441 are not set. |
| • | The air flow is more than 3 grams per second. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is more than 70°C (158°F). |
| • | The throttle position (TP) angle is between 4 percent and 56 percent for 20 seconds. |
| • | The engine run time is more than 30 seconds. |
Conditions For Setting The DTC
The O2S 1 voltage is between 399 mV and 499 mV for 125 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
| • | The vehicle will operate in an open loop operation. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
The normal scan tool voltage varies between 150 mV to 850 mV (0.15 volt to 0.85 volt) while in a closed loop operation.
An intermittent could be the result of the following conditions:
| • | A faulty electrical connection |
| • | Rubbed-through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Check for a faulty electrical connection or a damaged harness. Inspect the harness electrical connectors for the following conditions:
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
| • | A faulty terminal-to-wire connection |
| • | A damaged harness |
Replace the entire oxygen sensor (O2S 1) assembly. Do not attempt to repair the oxygen sensor if the following conditions exist:
| • | Damaged wiring |
| • | Damaged electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This step checks for proper sensor activity. When in closed loop fuel control, the O2S voltage should rapidly swing above and below the bias voltage.
-
This step checks the PCM and the HIGH and LOW circuits between the PCM and the O2S connector for proper operation.
-
This step checks for proper O2S heater circuit operation up to the O2S connector.
-
This step checks for proper circuit resistance between the O2S LOW circuit and PCM ground.
-
This step checks for proper circuit resistance between the O2S LOW circuit and PCM ground with a COLD sensor. A loose O2S or a faulty thread to the exhaust electrical contact will cause higher resistance when the O2S is cold. Although 500 ohms is allowed, typical resistance should be less than 50 ohms.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
Is the O2S voltage fixed within the specified voltage range? | 300-600 mV | |||||||||||
3 | This DTC is intermittent. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||
The leak may be very small and typically will be within 12 inches of the suspect O2S. Did you find and repair a problem? | -- | |||||||||||
5 |
Is the voltage less than the specified value? | 20 mV | ||||||||||
6 |
Is the resistance of the circuit less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | ||||||||||
Did you find and repair a problem? | -- | |||||||||||
Connect a test lamp between the O2S LOW circuit on the PCM side and the battery positive terminal. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | |||||||||||
9 |
Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | ||||||||||
10 | Repair the circuit that measured high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
11 | Repair the high resistance between the O2S LOW circuit and the engine ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Probable causes include the following:
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
12 | Replace the O2S sensor. Refer to Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
|
Important: Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||||||||||
14 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic passed? | -- | ||||||||||
15 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | System OK |
