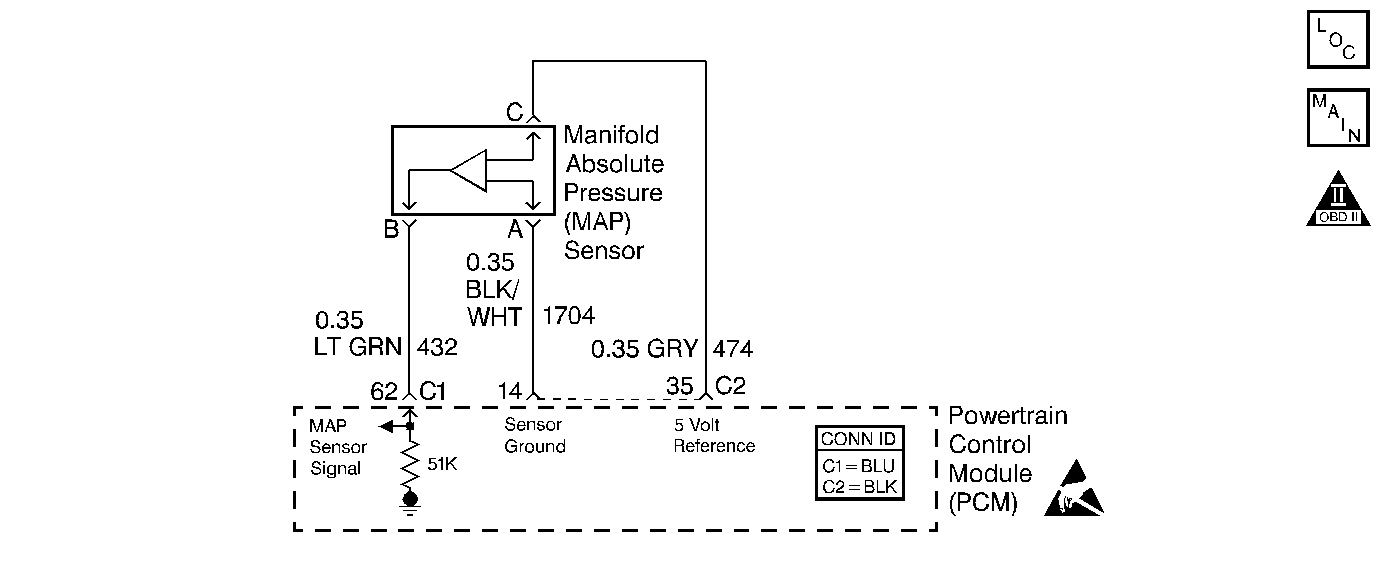
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor measures the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result from engine load, or the intake manifold vacuum, and RPM changes, and converts these into a voltage output. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) sends a 5 volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the sensor also changes. By monitoring the sensor output voltage, the PCM calculates the manifold pressure. A lower pressure, low voltage, output voltage will be approximately 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle. Higher pressure, high voltage, output voltage will be approximately 4.5 to 4.8 volts at wide open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is also used to measure barometric pressure, allowing the PCM to make adjustments for different altitudes. The PCM uses the MAP sensor to control fuel delivery and ignition timing.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
Important: Be sure to use the same diagnostic test equipment for all measurements.
-
The Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
This diagnostic table should not be used if any DTCs are set. You need to diagnosis any DTCs that are set first.
-
Applying 34 kPa (10 in of Hg) vacuum to the MAP sensor should cause the voltage to be 1.5 to 2.1 volts less than the voltage at step 3. Upon applying vacuum to the sensor, the change in the voltage should be instantaneous. A slow voltage change indicates a malfunctioning sensor.
-
Move the sensor electrical connector, by hand only, while watching the scan tool to check for an intermittent connection. Output that changes more than 0.10 volt indicates a bad connection.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||
Were any DTCs set? | -- | Go to ApplicableDTC Table | ||||||
3 | Compare the BARO reading with the reading of a known good vehicle. Are the BARO readings between the 2 vehicles within the specified value? | 3 kPa | ||||||
Is the difference more than the second specified value? | 34 kPa (10 in of Hg) 1.5 V | |||||||
5 | Check the MAP sensor vacuum source for the following conditions:
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||||||
6 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||
8 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
9 |
Does the system now operate properly? | -- | System OK |
