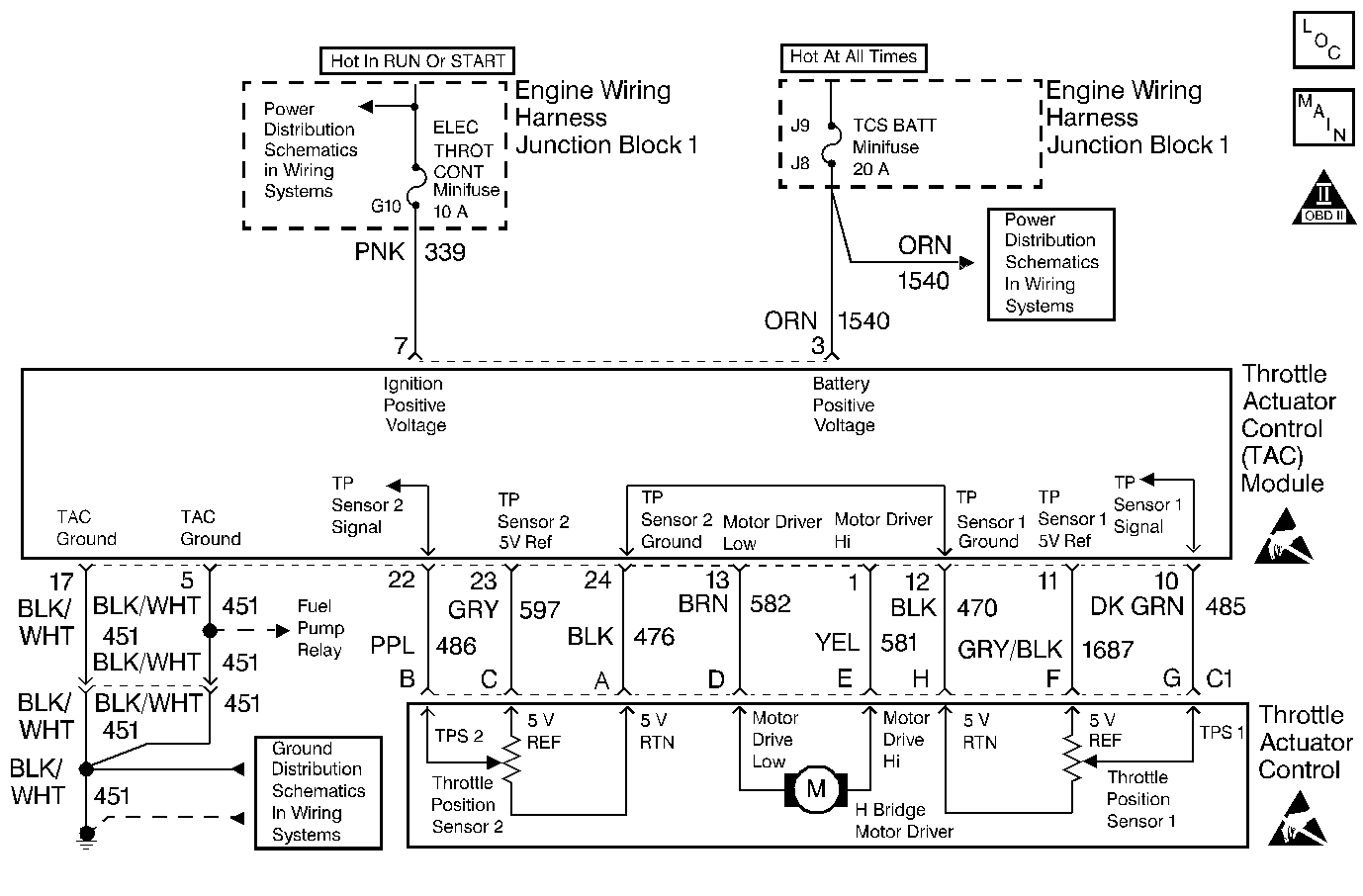
Circuit Description
The commanded throttle position, based on accelerator pedal position and possibly other limiting factors, is compared to the actual throttle position. The PCM monitors the Commanded and actual throttle position. This DTC sets if the PCM detects the problem.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No other ETC DTCs are set. |
| • | No PCM processor DTCs are present. |
| • | The ignition is in the crank or run position. |
| • | The ignition voltage is more than 8.5 volts with key ON engine OFF. |
| • | The ETC system is not in the battery saver mode. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects that the commanded and actual throttle positions are not within a calibrated range of each other.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the first trip in which the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | If equipped with traction control, the PCM will command the EBTCM via the serial data circuit to turn OFF traction control and illuminate the TRACTION OFF lamp. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect for the following:
Important: Ensure that the starting and charging systems are operating properly. Low system voltage causes this DTC to set.
If you do not find any trouble, check for mechanical problems or binding that may be temperature related. Components may not move freely in extreme heat or cold due to the presence of contaminants or ice formation.
Many situations may lead to an intermittent condition. Perform each inspection or test as directed.
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Loose terminal connection |
| - | Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the powertrain control module (PCM) and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
If the condition is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Snapshot or Freeze Frame/Failure Records may be useful in determining when the DTC or condition was identified.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If the TP indicated angle does not follow the movement of the throttle blade, and no TP sensor DTCs are set, there is a mechanical problem with the throttle shaft or the TP sensor. Replace the throttle body assembly. Re-install the air inlet duct after repairs are completed.
-
When the PCM detects a problem within the ETC System other DTCs may set due to the many redundant tests run continuously on this system. Locating and repairing one individual problem may correct more than one DTC. Keep this in mind when reviewing captured DTC info.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 |
Important: If you came from one of the following DTC tables continue with this table and go to step 3. Is DTC P1120, P1220 or P1221 set? | -- | Diagnose these DTCs first | |
Does the TP sensor 1 and 2 angle increase to near the specified value as the pedal is depressed and decrease as the pedal is released? | 100% | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
4 |
Does the voltage measure specified range? | 7.5-8.5 V | ||
5 |
Is any voltage present? | -- | ||
6 | Test for an open in each Throttle Actuator circuit (Motor Hi and Motor Low). Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
7 | Test for a short to ground on each Throttle Actuator circuit (Motor Hi and Motor Low). Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
8 | Test for continuity between each Throttle Actuator circuit (Motor Hi and Motor Low) and all other circuits in the TAC module connector. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is continuity indicated? | -- | ||
9 | Repair the short to voltage on the affected Throttle Actuator circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |
10 | Repair the open or high resistance on the affected Throttle Actuator circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |
11 | Repair the short to ground on the affected Throttle Actuator circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |
12 | Repair the circuits that are shorted together. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |
13 | Inspect for poor connections at the TAC module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
14 | Replace the TAC module. Refer to Accelerator Pedal Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
15 | Inspect for poor connections at the TAC. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
16 | Replace the throttle body/TAC assembly. Refer to Throttle Body Assembly Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
17 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool indicate any DTCs set that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC | System OK |
