Disc Brakes System Description Front
Front Brake Rotor
The front brake rotor is a machined, cast iron ventilated rotor. The rotor is cast with cooling fins between the friction surfaces. The internal fins or vanes radiate from the center of the rotor to the outer edge of the rotor. This design enables the rotor to act as its own cooling fan.
Front Brake Caliper
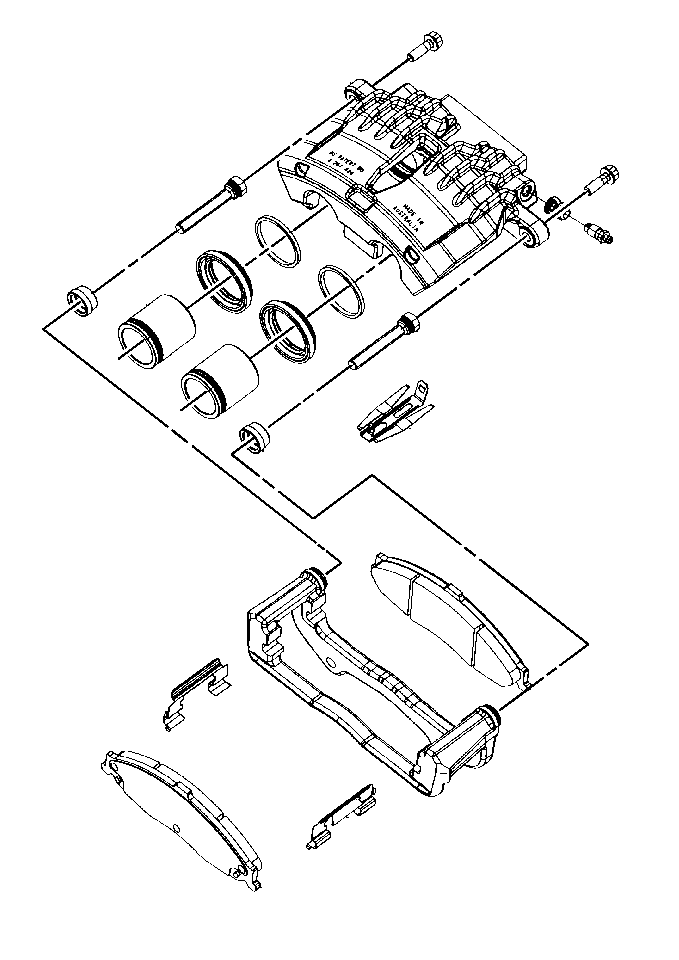
The aluminum dual piston front caliper used on this vehicle is mounted onto the front brake caliper mounting plate, and ultimately to the steering knuckle. Applying the brake pedal creates hydraulic pressure. This pressure exerts equally against the bottom of the pistons and against the bottom of the cylinder bores. The pressure applied to the pistons transmits to the inner pad and forces the pad against the inner rotor surface. The pressure applied to the bottom of the cylinders forces the caliper to slide in the caliper bolt bushings toward the center of the vehicle. This movement forces the outer section of the caliper against the back of the outer pad and presses the pad against the outer rotor surface. As hydraulic pressure builds, the pads press against the rotor surface with increasing force. The increasing force causes the vehicle to stop. In addition, it is this sliding action that allows a disc brake caliper to compensate for wear of the inner and outer pads. If upon inspection, it is found that one pad is significantly thicker or thinner than its counterpart, it would be an indication that the caliper is not sliding freely, and therefore not self-adjusting as it is should.
The brake caliper piston seals, while sealing the hydraulic circuit at the wheels, have a second function. These seals while firmly mounted in their channels, do distort very slightly under brake actuation. When the brakes are applied, the movement of the pistons out of the caliper bores distort the piston seals. When the brake pedal is released, the piston returns only as far as the seal was distorted. While this distortion of the seal shape is very minimal, it is enough to allow the brake pads to retract very slightly so as to eliminate any significant drag of the brakes.
Disc Brakes System Description Rear
Rear Brake Rotor
The rear brake rotor is a composite cast iron ventilated rotor. The rear brake rotor has a stamped sheet metal flange which is insert cast. The internal fins or vanes between the friction surfaces radiate from the center of the rotor to the outer edge of the rotor. This design enables the rotor to act as its own cooling fan.
Rear Brake Caliper
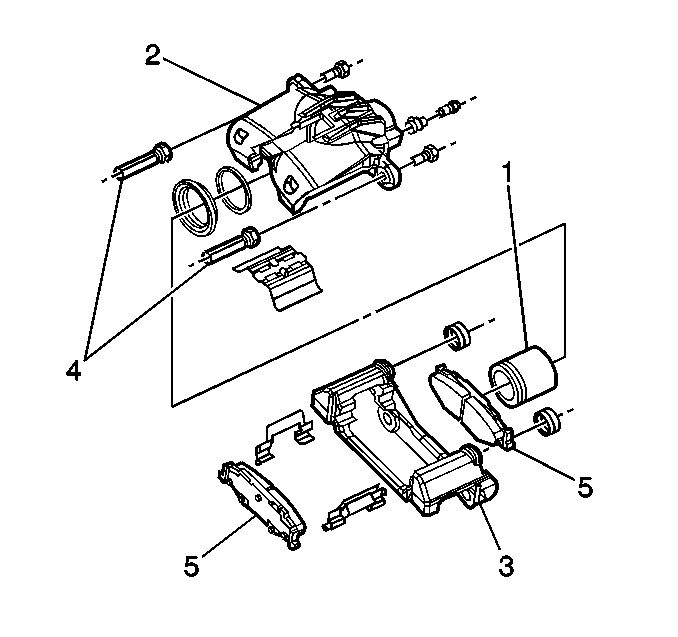
The rear brake caliper has a single piston (1) in an aluminum housing (2). The housing is suspended in an anchor bracket (3) on two guide pins (4). The caliper mounts to the steering knuckle with two mounting bolts. Applying the brake pedal creates hydraulic pressure. This pressure exerts equally against the bottom of the piston and against the bottom of the cylinder bore. The pressure applied to the piston transmits to the brake pads (5). The brake pads clamp down on the rotor, creating friction in order to stop the car.
Application of the parking brake causes the following components to move outward:
| • | The pushrod (23) |
| • | The actuating collar (10) |
| • | The clamp rod (19) |
The outward motion of the above components causes the caliper to move inward. Inward motion of the caliper forces the brake pads against the rotor in order to hold the vehicle in place. The parking brake mechanism is completely independent of the hydraulic braking system.
