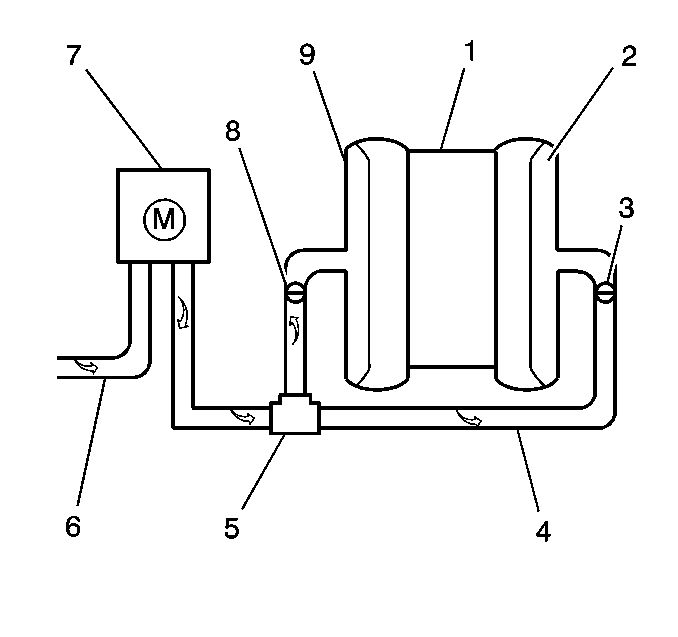
The Secondary Air Injection (AIR) system helps reduce Hydrocarbon
(HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) exhaust emissions.
It also heats up the 3-way catalytic converters quickly on engine
start-up so conversion of exhaust gases can occur sooner.